# Create a new annotation
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/annotations/create-a-new-annotation
openapi.json post /v0/annotations
Creates a new annotation.
# Delete an annotation
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/annotations/delete-an-annotation
openapi.json delete /v0/annotations/{id}
Deletes an existing annotation.
# Get a single annotation by ID
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/annotations/get-a-single-annotation-by-id
openapi.json get /v0/annotations/{id}
Retrieves detailed information about a specific annotation.
# List annotations
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/annotations/list-annotations
openapi.json get /v0/annotations
Retrieves a paginated list of annotations with optional filtering.
# Update an annotation
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/annotations/update-an-annotation
openapi.json put /v0/annotations/{id}
Updates an existing annotation.
# Create a new application
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/applications/create-a-new-application
openapi.json post /v0/applications
Creates a new application configuration.
# Get a single application by ID
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/applications/get-a-single-application-by-id
openapi.json get /v0/applications/{id}
Retrieves detailed information about a specific application.
# Get API keys for an application
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/applications/get-api-keys-for-an-application
openapi.json get /v0/applications/{id}/api-keys
Retrieves all API keys associated with a specific application.
# List applications
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/applications/list-applications
openapi.json get /v0/applications
Retrieves a paginated list of applications with optional filtering.
# List document chunks
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/document-chunks/list-document-chunks
openapi.json get /v0/documents/chunked
Retrieves a paginated list of document chunks with optional filtering by document ID.
# Get tags for a document
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/document-tags/get-tags-for-a-document
openapi.json get /v0/documents/{id}/tags
Retrieves all tags assigned to a specific document.
# Update document tags
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/document-tags/update-document-tags
openapi.json put /v0/documents/{id}/tags
Updates the tags assigned to a specific document. This replaces all existing tags.
# List document tests
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/document-tests/list-document-tests
openapi.json get /v0/documents/tests
Retrieves a paginated list of document tests with optional filtering by type and status
# Trigger document test
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/document-tests/trigger-document-test
openapi.json post /v0/documents/tests/trigger
Creates and triggers a document test execution. For KNOWLEDGE_COVERAGE and DOCS_TO_TASKS_MAPPING, applicationId is required.
# Activate a specific version of a document
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/document-versions/activate-a-specific-version-of-a-document
openapi.json put /v0/documents/{id}/versions/{versionNumber}/activate
Makes a specific version the active version of a document. This is the version that will be returned by default when fetching the document.
# Create a new version of a document
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/document-versions/create-a-new-version-of-a-document
openapi.json post /v0/documents/{id}/versions
Creates a new version of an existing document. The new version will have the next version number.
# Get a specific version of a document
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/document-versions/get-a-specific-version-of-a-document
openapi.json get /v0/documents/{id}/versions/{versionNumber}
Retrieves a specific version of a document by version number.
# List all versions of a document
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/document-versions/list-all-versions-of-a-document
openapi.json get /v0/documents/{id}/versions
Retrieves all versions of a specific document, ordered by version number descending.
# Add tags to multiple documents
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/documents/add-tags-to-multiple-documents
openapi.json post /v0/documents/tags
Add one or more tags to multiple documents in a single request. All documents and tags must exist and belong to the same organization.
# Assign a document to a user
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/documents/assign-a-document-to-a-user
openapi.json put /v0/documents/{id}/assign
Assigns a specific document to a user by their user ID.
# Bulk activate latest versions of multiple documents
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/documents/bulk-activate-latest-versions-of-multiple-documents
openapi.json post /v0/documents/activate-latest
Activates the latest version (highest version number) for multiple documents. Returns information about which documents were successfully activated and which failed.
# Bulk export documents as CSV
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/documents/bulk-export-documents-as-csv
openapi.json post /v0/documents/export/csv
Exports selected documents as a CSV file with title and content columns from active versions
# Bulk optimize multiple documents
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/documents/bulk-optimize-multiple-documents
openapi.json post /v0/documents/optimize
Triggers background optimization jobs for multiple documents. Returns information about which documents were successfully queued and which failed.
# Bulk update status of multiple document versions
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/documents/bulk-update-status-of-multiple-document-versions
openapi.json post /v0/documents/status
Updates the status of the active version for multiple documents.
# Create a new document
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/documents/create-a-new-document
openapi.json post /v0/documents
Creates a new document with the provided information.
# Delete a document
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/documents/delete-a-document
openapi.json delete /v0/documents/{id}
Deletes a document and its related document versions by the given document ID
# Delete multiple documents
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/documents/delete-multiple-documents
openapi.json post /v0/documents/delete
Deletes multiple documents by ID. This will also delete their versions.
# Get a single document by ID
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/documents/get-a-single-document-by-id
openapi.json get /v0/documents/{id}
Retrieves detailed information about a specific document, including its parent-child relationships and active version details.
# Get all document IDs
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/documents/get-all-document-ids
openapi.json get /v0/documents/ids
Fetches all document IDs without pagination. Supports filtering by status and tags. Useful for bulk operations.
# List documents
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/documents/list-documents
openapi.json get /v0/documents
Retrieves a paginated list of documents with optional filtering by status, assignee, parent, and other criteria. Only returns documents with active approved versions unless otherwise specified.
# Optimize a document
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/documents/optimize-a-document
openapi.json post /v0/documents/{id}/optimize
Triggers a background optimization job for the specified document. Returns 204 No Content on success.
# Update a document version
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/documents/update-a-document-version
openapi.json put /v0/documents/{id}/versions/{versionNumber}
Updates the content, title, status, or other fields of a specific document version.
# Create an evaluation definition
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/eval-definitions/create-an-evaluation-definition
openapi.json post /v0/definitions
Creates a new evaluation definition for an application.
# Delete an evaluation definition
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/eval-definitions/delete-an-evaluation-definition
openapi.json delete /v0/definitions/{id}
Deletes an evaluation definition and all associated data (cascade delete of linked tasks and evaluations).
# Link an evaluation definition to a task
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/eval-definitions/link-an-evaluation-definition-to-a-task
openapi.json post /v0/definitions/link
Associates an evaluation definition with a task for automatic evaluation.
# List evaluation definitions
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/eval-definitions/list-evaluation-definitions
openapi.json get /v0/definitions
Retrieves a paginated list of evaluation definitions for an application.
# Unlink an evaluation definition from a task
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/eval-definitions/unlink-an-evaluation-definition-from-a-task
openapi.json post /v0/definitions/unlink
Removes the association between an evaluation definition and a task.
# Update an evaluation definition
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/eval-definitions/update-an-evaluation-definition
openapi.json put /v0/definitions/{id}
Updates an existing evaluation definition.
# Update task-specific config for an evaluation definition
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/eval-definitions/update-task-specific-config-for-an-evaluation-definition
openapi.json put /v0/definitions/{id}/tasks/{taskId}
Updates the task-specific configuration (e.g., expected output) for an evaluation definition on a specific task.
# List tests
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/evals/list-tests
openapi.json get /v0/tests
Retrieves a paginated list of tests with optional filtering.
# Create an experiment
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/experiments/create-an-experiment
openapi.json post /v0/experiments
Creates a new experiment with the provided details.
# Create an experiment variant
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/experiments/create-an-experiment-variant
openapi.json post /v0/experiments/{id}/variants
Creates a new variant for the specified experiment.
# Get an experiment
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/experiments/get-an-experiment
openapi.json get /v0/experiments/{id}
Retrieves a single experiment by ID.
# List experiment variants
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/experiments/list-experiment-variants
openapi.json get /v0/experiments/{id}/variants
Retrieves a paginated list of variants for the specified experiment.
# List experiments
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/experiments/list-experiments
openapi.json get /v0/experiments
Retrieves a paginated list of experiments with optional filtering.
# Trigger experiment variant
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/experiments/trigger-experiment-variant
openapi.json post /v0/experiments/{id}/variants/{variantId}/trigger
Triggers execution of all tasks associated with the experiment for the specified variant. Returns 204 No Content on success.
# Update an experiment
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/experiments/update-an-experiment
openapi.json put /v0/experiments/{id}
Updates an existing experiment with the provided details.
# Update experiment variant
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/experiments/update-experiment-variant
openapi.json put /v0/experiments/{id}/variants/{variantId}
Updates a specific experiment variant. Only title, description, and configPatch can be updated.
# Create an inference step
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/inference-steps/create-an-inference-step
openapi.json post /v0/inference-steps
# List inference steps
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/inference-steps/list-inference-steps
openapi.json get /v0/inference-steps
# Ingest events
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/ingestion/ingest-events
openapi.json post /v0/ingest
Ingest an array of events (traces or steps) to store and process.
# Create a new issue
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/issues/create-a-new-issue
openapi.json post /v0/issues
Creates a new issue for tracking problems or improvements.
# Delete an issue
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/issues/delete-an-issue
openapi.json delete /v0/issues/{id}
Deletes an existing issue permanently.
# Get a single issue by ID
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/issues/get-a-single-issue-by-id
openapi.json get /v0/issues/{id}
Retrieves detailed information about a specific issue.
# List issues
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/issues/list-issues
openapi.json get /v0/issues
Retrieves a paginated list of issues with optional filtering by date range, status, priority, assignee, and more.
# Update an issue
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/issues/update-an-issue
openapi.json put /v0/issues/{id}
Updates an existing issue. Can be used to reassign, change status, update priority, or modify any other issue fields.
# Create a quickstart
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/quickstarts/create-a-quickstart
openapi.json post /v0/quickstarts
Creates a new quickstart
# Get a quickstart by ID
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/quickstarts/get-a-quickstart-by-id
openapi.json get /v0/quickstarts/{id}
Retrieves a single quickstart by its unique identifier
# List quickstarts
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/quickstarts/list-quickstarts
openapi.json get /v0/quickstarts
Retrieves a paginated list of quickstarts with optional filtering
# Update a quickstart
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/quickstarts/update-a-quickstart
openapi.json put /v0/quickstarts/{id}
Updates a quickstart by its unique identifier
# Create a new report
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/reports/create-a-new-report
openapi.json post /v0/reporting
Creates a new report.
# Delete a report
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/reports/delete-a-report
openapi.json delete /v0/reporting/{id}
Deletes a specific report by its ID.
# Get a single report
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/reports/get-a-single-report
openapi.json get /v0/reporting/{id}
Retrieves a specific report by its ID.
# Get columns for a datasource
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/reports/get-columns-for-a-datasource
openapi.json get /v0/reporting/datasources/{id}/columns
Returns metadata about the whitelisted columns for a specific datasource that can be used for filtering in reporting queries.
# Get context-aware columns for a datasource
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/reports/get-context-aware-columns-for-a-datasource
openapi.json post /v0/reporting/datasources/{id}/columns
Returns available columns for a datasource based on the intent and current query context. For filters/groupBy/measurements intents, returns all eligible columns. For orderBy intent, returns columns based on current groupBy and measurements context.
# Get distinct values for a column
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/reports/get-distinct-values-for-a-column
openapi.json get /v0/reporting/datasources/{id}/columns/{columnId}/values
Returns a list of distinct values from a specific column in a datasource. For relation columns (e.g., topicId), returns the related records with their IDs and display names.
# List available datasources
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/reports/list-available-datasources
openapi.json get /v0/reporting/datasources
Returns a list of all available reporting datasources with their IDs and human-readable names.
# List reports
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/reports/list-reports
openapi.json get /v0/reporting
Retrieves a paginated list of reports with optional filtering by date range, assignee, and application.
# Query reporting data
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/reports/query-reporting-data
openapi.json post /v0/reporting/query
Queries reporting data from specified datasources with optional filters and groupBy clauses. Supports aggregation and date truncation for time-based grouping.
# Update a report
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/reports/update-a-report
openapi.json put /v0/reporting/{id}
Updates an existing report. Can be used to update title, description, or reassign/unassign the report.
# Get a single run by ID
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/runs/get-a-single-run-by-id
openapi.json get /v0/runs/{id}
Retrieves detailed information about a specific run.
# List runs
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/runs/list-runs
openapi.json get /v0/runs
Retrieves a paginated list of runs with optional filtering.
# Create a scrape job
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/scrape-jobs/create-a-scrape-job
openapi.json post /v0/scrape-jobs
# Get a scrape job by ID
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/scrape-jobs/get-a-scrape-job-by-id
openapi.json get /v0/scrape-jobs/{id}
# List all scrape jobs
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/scrape-jobs/list-all-scrape-jobs
openapi.json get /v0/scrape-jobs
# Start scraping all pages of a scrape job
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/scrape-jobs/start-scraping-all-pages-of-a-scrape-job
openapi.json post /v0/scrape-jobs/{id}/start
# Update a scrape job
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/scrape-jobs/update-a-scrape-job
openapi.json put /v0/scrape-jobs/{id}
# Create a new style guide
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/style-guides/create-a-new-style-guide
openapi.json post /v0/style-guides
Creates a new style guide.
# Get a single style guide by ID
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/style-guides/get-a-single-style-guide-by-id
openapi.json get /v0/style-guides/{id}
Retrieves detailed information about a specific style guide.
# List style guides
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/style-guides/list-style-guides
openapi.json get /v0/style-guides
Retrieves a paginated list of style guides with optional filtering.
# Update a style guide
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/style-guides/update-a-style-guide
openapi.json put /v0/style-guides/{id}
Updates the content of an existing style guide.
# Create a new tag
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/tags/create-a-new-tag
openapi.json post /v0/tags
Creates a new tag with the provided information.
# Delete a tag
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/tags/delete-a-tag
openapi.json delete /v0/tags/{id}
Deletes a tag by ID. This will also remove the tag from all documents.
# Get a single tag by ID
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/tags/get-a-single-tag-by-id
openapi.json get /v0/tags/{id}
Retrieves detailed information about a specific tag.
# List tags
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/tags/list-tags
openapi.json get /v0/tags
Retrieves a paginated list of tags with optional search filtering.
# Update an existing tag
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/tags/update-an-existing-tag
openapi.json put /v0/tags/{id}
Updates an existing tag with the provided information.
# Create or update a task schedule
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/task-schedules/create-or-update-a-task-schedule
openapi.json post /v0/tasks/schedule
# Delete task schedule
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/task-schedules/delete-task-schedule
openapi.json delete /v0/tasks/{id}/schedule
# Get task schedule
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/task-schedules/get-task-schedule
openapi.json get /v0/tasks/{id}/schedule
# Get tags for a task
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/task-tags/get-tags-for-a-task
openapi.json get /v0/tasks/{id}/tags
Retrieves all tags assigned to a specific task.
# Update task tags
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/task-tags/update-task-tags
openapi.json put /v0/tasks/{id}/tags
Updates the tags assigned to a specific task. This replaces all existing tags.
# Add tags to multiple tasks
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/tasks/add-tags-to-multiple-tasks
openapi.json post /v0/tasks/tags
Add one or more tags to multiple tasks in a single request. All tasks and tags must exist and belong to the same organization.
# Bulk delete tasks
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/tasks/bulk-delete-tasks
openapi.json post /v0/tasks/delete
Deletes multiple tasks by their IDs.
# Create a new task
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/tasks/create-a-new-task
openapi.json post /v0/tasks
Creates a new task.
# Get a single task by ID
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/tasks/get-a-single-task-by-id
openapi.json get /v0/tasks/{id}
Retrieves detailed information about a specific task.
# Get task IDs
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/tasks/get-task-ids
openapi.json get /v0/tasks/ids
Retrieves a list of task IDs with optional filtering.
# Install a task template
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/tasks/install-a-task-template
openapi.json post /v0/tasks/template
Installs a predefined task template, creating tasks, topics, and eval definitions.
# List tasks
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/tasks/list-tasks
openapi.json get /v0/tasks
Retrieves a paginated list of tasks with optional filtering.
# Run a task
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/tasks/run-a-task
openapi.json post /v0/tasks/trigger
Triggers the execution of a task.
# Update an existing task
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/tasks/update-an-existing-task
openapi.json put /v0/tasks/{id}
Updates an existing task with the provided information.
# Get a single test by ID
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/tests/get-a-single-test-by-id
openapi.json get /v0/tests/{id}
Retrieves detailed information about a specific test.
# Create a new topic
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/topics/create-a-new-topic
openapi.json post /v0/topics
Creates a new topic.
# Get a single topic by ID
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/topics/get-a-single-topic-by-id
openapi.json get /v0/topics/{id}
Retrieves detailed information about a specific topic.
# List topics
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/topics/list-topics
openapi.json get /v0/topics
Retrieves a paginated list of topics with optional filtering.
# Get a single trace by ID
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/traces/get-a-single-trace-by-id
openapi.json get /v0/traces/{id}
Retrieves detailed information about a specific trace.
# Get a single trace by Test ID
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/traces/get-a-single-trace-by-test-id
openapi.json get /v0/traces/by-test/{id}
Retrieves detailed information about a specific trace.
# List Traces
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/traces/list-traces
openapi.json get /v0/traces
Retrieve traces with associated steps, filtered by application ID and optional date parameters.
# Delete webhook configuration for an application
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/webhook/delete-webhook-configuration-for-an-application
openapi.json delete /v0/applications/{id}/webhook
Deletes the webhook configuration for a specific application.
# Get webhook configuration for an application
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/webhook/get-webhook-configuration-for-an-application
openapi.json get /v0/applications/{id}/webhook
Retrieves the webhook configuration for a specific application. Returns null if no webhook is configured.
# Test webhook configuration for an application
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/webhook/test-webhook-configuration-for-an-application
openapi.json post /v0/webhook/test
Sends a test webhook request to the configured webhook URL with a sample payload. Returns success status and any error details.
# Validate an incoming webhook request
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/api-reference/webhook/validate-an-incoming-webhook-request
openapi.json post /v0/validate-webhook
Checks the body (including timestamp and signature) against the configured webhook secret. Returns `{ valid: true }` if the signature is valid.
# Changelog
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/changelog
Track product releases and improvements across Avido versions.
Avido v0.4.0 introduces Experiments: A structured framework for testing prompt, model, and parameter changes against your evaluation tasks before deploying to production. This release empowers teams to iterate confidently on AI configurations with clear comparison metrics and zero risk of silent regressions.
## Experiments
Experiments enable systematic testing of configuration changes across your evaluation tasks. Create controlled tests for prompts, models, and parameters, compare results against baselines, and make data-driven decisions about what to deploy.
### Key Capabilities
* **Baseline-First Workflow**: Establish performance benchmarks before testing any changes, ensuring valid comparisons
* **Single-Variable Testing**: Each variant changes exactly one parameter (prompt, temperature, model, etc.) for clear cause-and-effect analysis
* **Automatic Isolation**: Experiment data is completely separated from production metrics and reporting
* **In-App Execution**: All tests run inside your application using the same webhook as regular evaluations—no separate infrastructure needed
* **Full Audit Trail**: Track every configuration change, test run, and decision with complete version history
### Why We Built This
Configuration changes to AI systems carry hidden risks. A temperature adjustment, prompt refinement, or model upgrade can improve some outputs while breaking others. Without structured testing, teams either move too slowly (afraid of regressions) or too quickly (missing quality issues until production).
**For Engineering Teams**: Test changes systematically before deploying. Run variants on the same task set as your baseline, get clear delta metrics, and avoid shipping regressions.
**For Product Teams**: Make evidence-based decisions about AI quality improvements. See exactly how prompt changes affect task performance across your evaluation suite.
**For Compliance Teams**: Maintain a complete audit trail of what was tested, why, and what changed. Every experiment documents the hypothesis, configuration changes, and results—meeting regulatory requirements for AI system changes.
Avido v0.3.0 delivers a streamlined set of improvements focused on helping teams organize work more efficiently and maintain consistent AI behavior across applications. This release strengthens how tasks and documents are structured, how teams perform bulk operations, and how style guides flow through both the Avido UI and your own applications.
## New in This Release
* **Unified Tagging System**: Add tags to tasks and documents, filter by tag, and apply tags in bulk.
* **Bulk Actions**: Perform shared bulk operations across tasks and documents, including bulk delete.
* **Document CSV Export**: Export all imported documents directly to CSV/TXT from the UI.
* **Style Guide Management**: Create and manage style guides directly in the UI—Avido automatically uses the latest version in evals, or you can pull them into your own app via API.
* **New Scraping Experience**: Scrape websites with full URL visibility, single-call backend processing, automatic “scrape job” creation, and protection against duplicate triggers.
![v0.2.0 update]() Avido v0.2.0 introduces Document Versioning and Knowledge Base Testing�powerful features that enable teams to maintain stable production content while continuously improving their AI knowledge bases. This release empowers organizations to collaborate on documentation updates without risking production stability, while systematically identifying and fixing knowledge gaps.
## Document Versioning
Document versioning provides comprehensive version control for your AI knowledge base, ensuring production stability while enabling continuous improvement. Teams can now iterate on content safely, with clear workflows that separate work-in-progress from production-ready documentation.
### Key Capabilities
* **Four-State Version Lifecycle**: Documents support Approved (production), Draft (work-in-progress), Review (pending approval), and Archived (historical) states
* **Production Stability by Default**: APIs and AI responses use only approved versions unless explicitly requested otherwise
* **Collaborative Workflows**: Multiple team members can work on drafts simultaneously with version notes and clear approval processes
* **Complete Audit Trail**: Track who made changes, when, and why�critical for compliance requirements
### Why We Built This
Document Versioning and Knowledge Base Testing work together to create a robust content management system that balances stability with continuous improvement. Teams in regulated industries now have the tools to maintain high-quality, evolving documentation that powers AI systems�with the confidence that changes won't compromise production stability or compliance requirements.
**For Content Teams**: Safely iterate on documentation without affecting production systems. Create drafts from any document version, collaborate with teammates, and deploy updates only when ready.
**For Engineering Teams**: Maintain API stability while content evolves. Production systems automatically use only approved content, with optional access to draft versions for testing.
**For Compliance Teams**: Full version history with user attribution meets regulatory requirements. Track every change with clear audit trails and approval workflows.
## Knowledge Base Testing
Systematic testing ensures your knowledge base remains comprehensive and consistent. Two new test types help identify gaps and conflicts before they impact your AI applications.
### Document Coverage Test
Automatically identifies gaps in your knowledge base by testing how well your documents cover defined tasks. This ensures AI agents have the information needed to handle all scenarios effectively.
### Overlap and Contradictions Analysis
Tests your knowledge base using the Overlap and Contradictions test to identify:
* **Overlapping Information**: Find redundant content across documents
* **Contradictory Instructions**: Detect conflicting guidance that could confuse AI agents
Avido v0.2.0 introduces Document Versioning and Knowledge Base Testing�powerful features that enable teams to maintain stable production content while continuously improving their AI knowledge bases. This release empowers organizations to collaborate on documentation updates without risking production stability, while systematically identifying and fixing knowledge gaps.
## Document Versioning
Document versioning provides comprehensive version control for your AI knowledge base, ensuring production stability while enabling continuous improvement. Teams can now iterate on content safely, with clear workflows that separate work-in-progress from production-ready documentation.
### Key Capabilities
* **Four-State Version Lifecycle**: Documents support Approved (production), Draft (work-in-progress), Review (pending approval), and Archived (historical) states
* **Production Stability by Default**: APIs and AI responses use only approved versions unless explicitly requested otherwise
* **Collaborative Workflows**: Multiple team members can work on drafts simultaneously with version notes and clear approval processes
* **Complete Audit Trail**: Track who made changes, when, and why�critical for compliance requirements
### Why We Built This
Document Versioning and Knowledge Base Testing work together to create a robust content management system that balances stability with continuous improvement. Teams in regulated industries now have the tools to maintain high-quality, evolving documentation that powers AI systems�with the confidence that changes won't compromise production stability or compliance requirements.
**For Content Teams**: Safely iterate on documentation without affecting production systems. Create drafts from any document version, collaborate with teammates, and deploy updates only when ready.
**For Engineering Teams**: Maintain API stability while content evolves. Production systems automatically use only approved content, with optional access to draft versions for testing.
**For Compliance Teams**: Full version history with user attribution meets regulatory requirements. Track every change with clear audit trails and approval workflows.
## Knowledge Base Testing
Systematic testing ensures your knowledge base remains comprehensive and consistent. Two new test types help identify gaps and conflicts before they impact your AI applications.
### Document Coverage Test
Automatically identifies gaps in your knowledge base by testing how well your documents cover defined tasks. This ensures AI agents have the information needed to handle all scenarios effectively.
### Overlap and Contradictions Analysis
Tests your knowledge base using the Overlap and Contradictions test to identify:
* **Overlapping Information**: Find redundant content across documents
* **Contradictory Instructions**: Detect conflicting guidance that could confuse AI agents
![v0.1.0 update]() Avido v0.1.0 introduces the System Journal—an intelligent monitoring system that automatically tracks and documents all significant changes in your AI deployments. This release also includes performance improvements and stability fixes to make Avido more reliable in production.
The System Journal acts as a "black box recorder" for your AI systems, capturing every meaningful change that could impact model behavior, compliance, or evaluation accuracy. Small changes to AI configurations can cause unexpected regressions—a model version bump, temperature adjustment, or prompt tweak can break functionality in unexpected ways.
### Key Features
* **Automatic Change Detection**: Identifies when model parameters (temperature, max tokens, top-k, etc.) change between deployments
* **Missing Parameter Alerts**: Flags when critical parameters required for evaluation or compliance are absent
* **Intelligent Journal Entries**: Generates human-readable descriptions of what changed, when, and by how much
* **Complete Audit Trail**: Maintains a tamper-proof history for regulatory compliance
* **Zero Manual Overhead**: Operates completely automatically in the background
### Why We Built This
**For Engineering Teams**: Prevent configuration drift, accelerate incident response, and maintain evaluation integrity. Know immediately when model parameters change unexpectedly.\
**For Compliance Teams**: Achieve regulatory readiness with comprehensive audit trails, track risk-relevant parameter changes, and reduce compliance reporting time from weeks to minutes.
## Improvements and Fixes
* Manage multiple evaluations per task simultaneously
* Schedule evaluations with custom criticality levels and intervals
* System journal entries are now visible in dashboard graphs
* Performance optimizations for faster response times
* Enhanced security for production deployments
Avido v0.1.0 introduces the System Journal—an intelligent monitoring system that automatically tracks and documents all significant changes in your AI deployments. This release also includes performance improvements and stability fixes to make Avido more reliable in production.
The System Journal acts as a "black box recorder" for your AI systems, capturing every meaningful change that could impact model behavior, compliance, or evaluation accuracy. Small changes to AI configurations can cause unexpected regressions—a model version bump, temperature adjustment, or prompt tweak can break functionality in unexpected ways.
### Key Features
* **Automatic Change Detection**: Identifies when model parameters (temperature, max tokens, top-k, etc.) change between deployments
* **Missing Parameter Alerts**: Flags when critical parameters required for evaluation or compliance are absent
* **Intelligent Journal Entries**: Generates human-readable descriptions of what changed, when, and by how much
* **Complete Audit Trail**: Maintains a tamper-proof history for regulatory compliance
* **Zero Manual Overhead**: Operates completely automatically in the background
### Why We Built This
**For Engineering Teams**: Prevent configuration drift, accelerate incident response, and maintain evaluation integrity. Know immediately when model parameters change unexpectedly.\
**For Compliance Teams**: Achieve regulatory readiness with comprehensive audit trails, track risk-relevant parameter changes, and reduce compliance reporting time from weeks to minutes.
## Improvements and Fixes
* Manage multiple evaluations per task simultaneously
* Schedule evaluations with custom criticality levels and intervals
* System journal entries are now visible in dashboard graphs
* Performance optimizations for faster response times
* Enhanced security for production deployments
![v0.0.5 update]() Optimise your articles for RAG straight in Avido – use our best practices to process your original knowledge base, help site or similar into split, optimised articles with proper metadata, ready to ingest into RAG. Much more to come!
### 📖 Recall (RAG Evaluation)
The **Recall** feature in Avido provides a comprehensive way to assess how well your AI application's Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) system is performing.
* Measure key aspects of quality, correctness, and relevancy within your RAG workflow.
* **No-code interface** empowers both technical and non-technical stakeholders to interpret metrics.
* Ensure systems meet required quality standards before production.
### 🛠️ SDK & Trace Improvements
* Micro-second precision when ingesting data.
* Group traces to visualise workflow structure at a glance.
### ☁️ OpenAI on Azure Support
* EU customers can now run all inference on models hosted in Europe.
* Regardless of geography, we, or any of our providers, never train on any data.
### 🐞 Bug Fixes & Polishing
Lots of improvements and paper cuts to make your experience with Avido even smoother, faster, and enjoyable.
Optimise your articles for RAG straight in Avido – use our best practices to process your original knowledge base, help site or similar into split, optimised articles with proper metadata, ready to ingest into RAG. Much more to come!
### 📖 Recall (RAG Evaluation)
The **Recall** feature in Avido provides a comprehensive way to assess how well your AI application's Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) system is performing.
* Measure key aspects of quality, correctness, and relevancy within your RAG workflow.
* **No-code interface** empowers both technical and non-technical stakeholders to interpret metrics.
* Ensure systems meet required quality standards before production.
### 🛠️ SDK & Trace Improvements
* Micro-second precision when ingesting data.
* Group traces to visualise workflow structure at a glance.
### ☁️ OpenAI on Azure Support
* EU customers can now run all inference on models hosted in Europe.
* Regardless of geography, we, or any of our providers, never train on any data.
### 🐞 Bug Fixes & Polishing
Lots of improvements and paper cuts to make your experience with Avido even smoother, faster, and enjoyable.
![v0.0.4 update]() We're excited to announce the latest product updates for Avido. Our newest features make it easier and safer to deploy Generative AI, providing peace-of-mind for critical applications.
### 🔍 Enhanced Test View
* Easily dive into each evaluation to pinpoint exactly what's working—and what needs improvement.
* Clearly understand AI performance to rapidly iterate and optimize.
### 📌 System Journal
* Track application changes seamlessly and visualize how these updates impact individual eval performance.
* Stay informed and make confident deployment decisions with clear version tracking.
### 🔐 Single Sign-On (SSO)
* Support for all major identity providers, making it even easier to roll out Avido in enterprises.
### ⚙️ Custom Evaluations
* Create custom evals directly from our UI or via API.
* Test specific business logic, compliance requirements, brand-specific wording, and other critical aspects of your application, ensuring unmatched accuracy and reliability.
With these updates, Avido continues to empower financial services by ensuring safe, transparent, and high-quality deployment of Generative AI.
We're excited to announce the latest product updates for Avido. Our newest features make it easier and safer to deploy Generative AI, providing peace-of-mind for critical applications.
### 🔍 Enhanced Test View
* Easily dive into each evaluation to pinpoint exactly what's working—and what needs improvement.
* Clearly understand AI performance to rapidly iterate and optimize.
### 📌 System Journal
* Track application changes seamlessly and visualize how these updates impact individual eval performance.
* Stay informed and make confident deployment decisions with clear version tracking.
### 🔐 Single Sign-On (SSO)
* Support for all major identity providers, making it even easier to roll out Avido in enterprises.
### ⚙️ Custom Evaluations
* Create custom evals directly from our UI or via API.
* Test specific business logic, compliance requirements, brand-specific wording, and other critical aspects of your application, ensuring unmatched accuracy and reliability.
With these updates, Avido continues to empower financial services by ensuring safe, transparent, and high-quality deployment of Generative AI.
![v0.0.3 update]() We're thrilled to share our first public changelog, marking a step forward in our commitment to enhancing the understanding of AI applications and helping enterprises maximize the value of AI with Avido.
### 🚀 Quickstart Workflow
* Upload existing outputs via CSV to automatically generate evaluation cases
* Smart AI-powered categorization of topics and tasks
* Interactive review interface for selecting benchmark outputs
* Automated evaluation criteria generation based on selected examples
### 📊 Improved Scoring System
* Simplified scoring scale (1-5) for more intuitive evaluation
* Updated benchmarking system for better quality assessment
* Refined evaluation criteria for clearer quality metrics
### 🤖 Smart Analysis
* Automatic topic detection from output patterns
* Task identification based on user intentions
* Intelligent grouping of similar outputs
* Automated quality scoring of historical outputs
### 💡 Enhanced Review Experience
* Visual topic distribution analysis
* Side-by-side conversation comparison
* Guided selection of benchmark outputs
* Contextual feedback collection for evaluation criteria
# Documents
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/documents
Knowledge management system for creating, versioning, and optimizing RAG-ready content
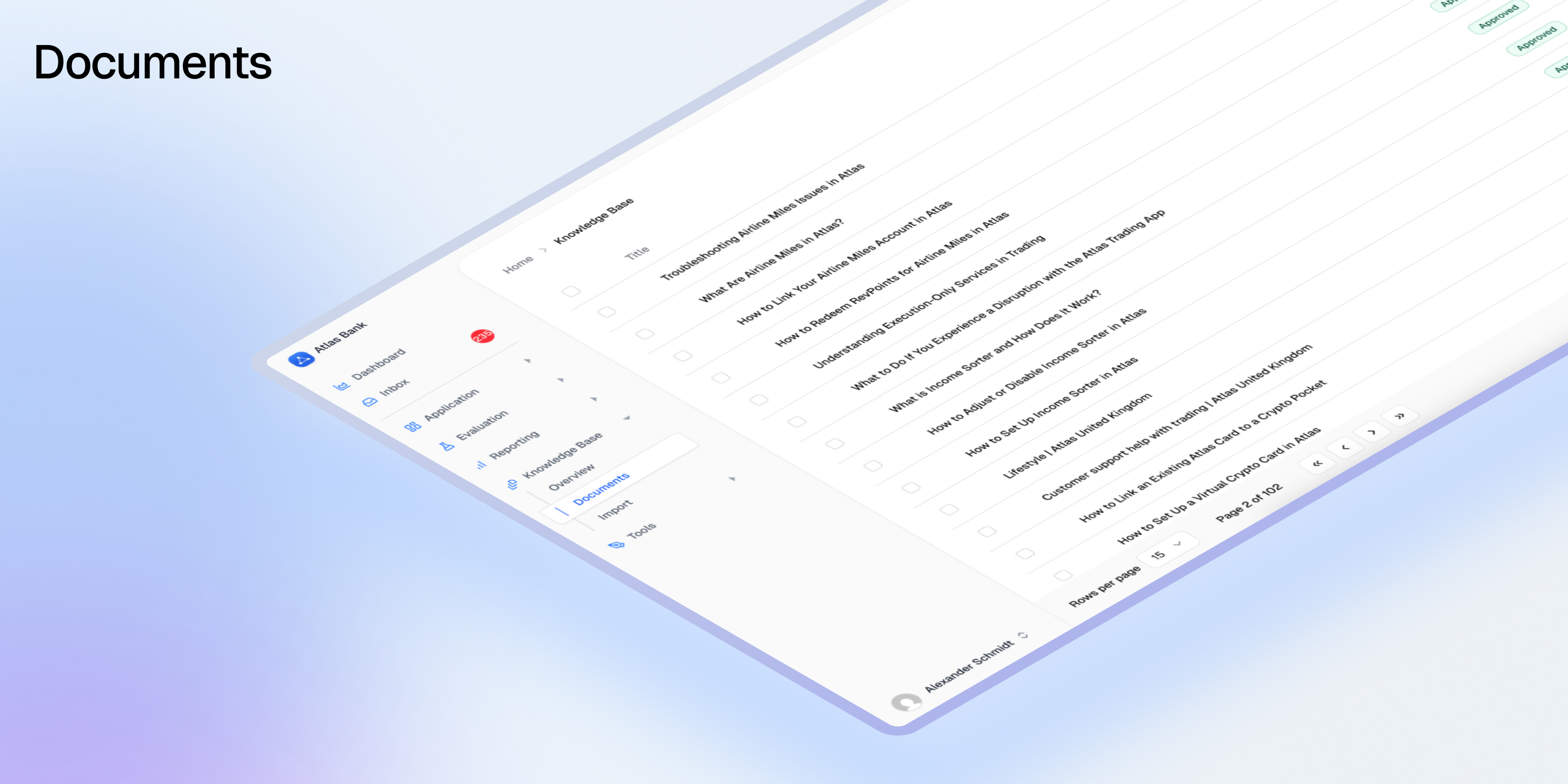
The Documents tool allows you to easily format and split your content into RAG-ready documents. It's your central knowledge base where teams can collaborate on creating, refining, and approving the content that powers your AI application. Whether you're building customer support bots, internal knowledge assistants, or any RAG-based system, Documents ensures your content is properly structured, versioned, and optimized for AI retrieval.
## What are Documents?
Documents in Avido are structured content pieces designed specifically for Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems. Unlike traditional document management, Avido Documents are:
* **AI-Optimized**: Automatically chunked and formatted for optimal retrieval
* **Version-Controlled**: Maintain approved versions in production while working on improvements
* **Collaborative**: Multiple team members can work on drafts without affecting live content
* **Traceable**: Every change is tracked for compliance and quality control
## Key Features
### Document Creation & Import
Documents can be created in multiple ways:
* **Manual Creation**: Write and format content directly in the Avido editor
* **Web Scraping**: Import content from any public URL
* **File Upload**: Upload existing documents (coming soon)
* **API Integration**: Programmatically create and manage documents
### AI-Powered Optimization
The platform includes intelligent document optimization that:
* **Reformats for RAG**: Structures content for better chunking and retrieval
* **Improves Clarity**: Enhances readability while preserving meaning
* **Maintains Consistency**: Ensures uniform formatting across your knowledge base
* **Preserves Intent**: Keeps the original message and tone intact
### Version Management
Every document supports comprehensive versioning:
#### Version States
* **APPROVED**: Live production version served by APIs
* **DRAFT**: Work-in-progress version for collaboration
* **REVIEW**: Pending approval from designated reviewers
* **ARCHIVED**: Historical versions for reference
#### Version Workflow
1. Create new versions from any existing version
2. Collaborate on drafts without affecting production
3. Submit for review when ready
4. Approve to make it the live version
5. Previous approved versions are automatically archived
### Approval Workflow
Documents can require approval before going live:
* **Assign Reviewers**: Designate who needs to approve changes
* **Email Notifications**: Reviewers are notified when approval is needed
* **Audit Trail**: Track who approved what and when
* **Compliance Ready**: Meet regulatory requirements for content control
## Using Documents
### Creating Your First Document
1. Navigate to the **Documents** section in your Avido dashboard
2. Click **New Document**
3. Choose your creation method:
* **Write**: Start with the built-in editor
* **Import from URL**: Scrape content from a website
* **Upload**: Import existing files (if enabled)
### Document Editor
The editor provides a rich set of formatting tools:
* **Markdown Support**: Write in markdown for quick formatting
* **Visual Editor**: Use the toolbar for formatting without markdown knowledge
* **Preview Mode**: See how your document will appear to users
* **Auto-Save**: Never lose your work with automatic saving
### Working with Versions
#### Creating a New Version
1. Open any document
2. Click **Create New Version** in the version sidebar
3. Add version notes describing your changes
4. Edit the content as needed
5. Save as draft or submit for review
#### Version History Sidebar
The sidebar shows:
* All versions with their status badges
* Creator and approval information
* Version notes and timestamps
* Quick actions for each version
#### Comparing Versions
1. Select two versions to compare
2. View side-by-side differences
3. See what was added, removed, or changed
4. Understand the evolution of your content
### Document Optimization
Use AI to improve your documents:
1. Open any document
2. Click **Optimize Document**
3. Review the AI-suggested improvements
4. Accept, reject, or modify suggestions
5. Save the optimized version
The optimizer helps with:
* Breaking content into logical sections
* Improving readability and clarity
* Standardizing formatting
* Enhancing retrieval effectiveness
### API Access
Documents are accessible via the Avido API:
```bash theme={null}
# Get all approved documents
GET /v0/documents
Authorization: Bearer YOUR_API_KEY
# Get a specific document
GET /v0/documents/{id}
# Include draft versions
GET /v0/documents?include_drafts=true
# Create a new document
POST /v0/documents
Content-Type: application/json
{
"title": "Product FAQ",
"content": "# Frequently Asked Questions...",
"metadata": {
"category": "support",
"product": "main"
}
}
```
### Integration with Testing
Documents integrate seamlessly with Avido's testing framework:
* **Knowledge Coverage**: Test if your documents cover all required topics
* **MECE Analysis**: Ensure content is Mutually Exclusive and Collectively Exhaustive
* **Task Mapping**: Verify documents address all user tasks
Tests automatically use approved versions unless configured otherwise.
## Best Practices
### Content Organization
* **Use Clear Titles**: Make documents easily discoverable
* **Add Metadata**: Tag documents with categories, products, or teams
* **Structure Hierarchically**: Use headings to create logical sections
* **Keep Focused**: One topic per document for better retrieval
### Version Management
* **Document Changes**: Always add clear version notes
* **Review Before Approval**: Have subject matter experts review changes
* **Test Before Production**: Run coverage tests on new versions
* **Archive Strategically**: Keep important historical versions accessible
### Collaboration
* **Assign Ownership**: Each document should have a clear owner
* **Use Draft Status**: Work on improvements without affecting production
* **Communicate Changes**: Notify stakeholders of significant updates
* **Regular Reviews**: Schedule periodic content audits
### RAG Optimization
* **Chunk-Friendly Content**: Write in digestible sections
* **Avoid Redundancy**: Don't duplicate information across documents
* **Use Examples**: Include concrete examples for better context
* **Update Regularly**: Keep content current and accurate
## Document Lifecycle
### 1. Creation Phase
* Identify knowledge gaps
* Create initial content
* Format for readability
* Add relevant metadata
### 2. Optimization Phase
* Run AI optimization
* Test with knowledge coverage
* Refine based on feedback
* Ensure completeness
### 3. Review Phase
* Submit for approval
* Gather stakeholder feedback
* Make necessary revisions
* Document decisions
### 4. Production Phase
* Approve for production use
* Monitor retrieval performance
* Track usage in traces
* Gather user feedback
### 5. Maintenance Phase
* Regular content audits
* Update outdated information
* Create new versions as needed
* Archive obsolete content
## Advanced Features
### Traceability
When documents are used in AI responses, Avido tracks:
* Which documents were retrieved
* How they influenced the response
This creates a feedback loop for continuous improvement.
## Getting Started
1. **Define Your Knowledge Base**: Identify what content your AI needs
2. **Create Initial Documents**: Start with your most critical content
3. **Optimize and Test**: Use AI optimization and run coverage tests
4. **Review and Approve**: Get stakeholder sign-off
5. **Monitor and Iterate**: Track usage and improve based on feedback
Documents transform static knowledge into dynamic, AI-ready content that evolves with your application's needs, ensuring your AI always has access to accurate, approved, and optimized information.
# Evaluations
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/evaluations
Built-in and custom evaluation types to measure AI quality, safety, and performance.
## Overview
Avido provides six evaluation types to measure different aspects of AI quality. Each evaluation is applied to tasks, then runs automatically when those tasks execute, providing actionable insights when quality standards aren't met.
| Evaluation Type | Purpose | Score Range | Pass Threshold |
| ---------------- | -------------------------------- | ----------- | -------------- |
| **Naturalness** | Human-like communication quality | 1-5 | 3.5 |
| **Style** | Brand guideline compliance | 1-5 | 3.5 |
| **Recall** | RAG pipeline performance | 0-1 | 0.5 |
| **Fact Checker** | Factual accuracy vs ground truth | 0-1 | 0.8 |
| **Custom** | Domain-specific criteria | 0-1 | 0.5 |
## Naturalness
Measures how natural, engaging, and clear your AI's responses are to users.
### What It Evaluates
The Naturalness evaluation assesses five dimensions of response quality:
* **Coherence** – Logical flow and consistency of ideas
* **Engagingness** – Ability to capture and maintain user interest
* **Naturalness** – Human-like language and tone
* **Relevance** – On-topic responses that address the user's intent
* **Clarity** – Clear, understandable language without ambiguity
### How It Works
An LLM evaluates your AI's response across all five dimensions on a 1-5 scale. The overall score is the average of these dimensions.
**Pass Criteria:**
* All five dimensions must score ≥ 3.5
* Average score ≥ 3.5
This ensures no single dimension fails even if the overall average is high.
### Example Results
| Coherence | Engagingness | Naturalness | Relevance | Clarity | Overall | Result |
| --------- | ------------ | ----------- | --------- | ------- | ------- | ----------------------- |
| 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5.0 | ✅ Pass |
| 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4.0 | ✅ Pass |
| 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 2 | 4.4 | ❌ Fail (Clarity \< 3.5) |
### When to Use
* Conversational AI and chatbots
* Customer support automation
* Content generation systems
* Any user-facing AI interactions
## Style
Evaluates whether responses adhere to your organization's style guidelines and brand voice.
### What It Evaluates
A single comprehensive score (1-5) based on your custom style guide, measuring:
* Tone and voice consistency
* Terminology usage
* Format and structure requirements
* Brand-specific guidelines
* Reading level and complexity
### How It Works
You provide a style guide document that defines your brand's communication standards. An LLM evaluates each response against this guide and provides:
* A score from 1-5
* Detailed analysis explaining the rating
**Pass Criteria:**
* Score ≥ 3.5
### Example Style Guide Elements
```markdown theme={null}
# Customer Support Style Guide
**Tone:** Professional yet friendly, never casual
**Voice:** Active voice preferred, clear and direct
**Terminology:** Use "account" not "profile", "transfer" not "send"
**Format:** Start with acknowledgment, provide solution, end with offer to help
**Constraints:** Keep responses under 100 words when possible
```
### When to Use
* Brand-critical communications
* Multi-channel consistency (chat, email, voice)
* Customer-facing applications where brand matters
Note: For regulated industries with strict compliance requirements, use Custom evaluations instead.
## Recall (RAG Evaluation)
Comprehensive evaluation of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) pipeline quality.
### What It Evaluates
Four metrics that measure different aspects of RAG performance:
* **Context Relevancy** – Are retrieved documents relevant to the query?
* **Context Precision** – How well-ranked are the retrieved documents?
* **Faithfulness** – Is the answer grounded in the retrieved context?
* **Answer Relevancy** – Does the answer address the user's question?
### How It Works
Each metric produces a score from 0-1 (higher is better). The overall score is the average of Context Precision, Faithfulness, and Answer Relevancy.
**Pass Criteria:**
* Context Precision ≥ 0.5
* Faithfulness ≥ 0.5
* Answer Relevancy ≥ 0.5
Note: Context Relevancy is computed for observability but doesn't affect pass/fail status.
### Score Interpretation
| Score Range | Interpretation | Action Required |
| ----------- | --------------------- | ----------------------- |
| 0.8 - 1.0 | Excellent performance | Monitor |
| 0.5 - 0.8 | Acceptable quality | Optimize if critical |
| 0.0 - 0.5 | Poor performance | Investigate immediately |
### Common Issues and Solutions
| Low Metric | Likely Cause | Solution |
| ----------------- | ------------------------------------ | ---------------------------------------------- |
| Context Precision | Too many irrelevant chunks retrieved | Reduce top\_k, improve filters |
| Context Relevancy | Embedding/index drift | Retrain embeddings, update index |
| Faithfulness | Model hallucinating | Add grounding instructions, reduce temperature |
| Answer Relevancy | Answer drifts off-topic | Improve prompt focus, add constraints |
### When to Use
* Knowledge base search and retrieval
* Document Q\&A systems
* RAG pipelines
* Any system combining retrieval with generation
## Fact Checker
Validates factual accuracy of AI responses against ground truth.
### What It Evaluates
Compares AI-generated statements with known correct information, classifying each statement as:
* **True Positives (TP)** – Correct facts present in the response
* **False Positives (FP)** – Incorrect facts in the response
* **False Negatives (FN)** – Correct facts omitted from the response
### How It Works
An LLM extracts factual statements from both the AI response and ground truth, then classifies them. The F1 score measures accuracy:
```
F1 = TP / (TP + 0.5 × (FP + FN))
```
**Pass Criteria:**
* F1 score ≥ 0.8
This allows high-quality answers with minor omissions while maintaining strict accuracy standards.
### Example Classification
**Question:** "What powers the sun?"
**Ground Truth:** "The sun is powered by nuclear fusion. In its core, hydrogen atoms fuse to form helium, releasing tremendous energy."
**AI Response:** "The sun is powered by nuclear fission, similar to nuclear reactors, and provides light to the solar system."
**Classification:**
* TP: \["Provides light to the solar system"]
* FP: \["Powered by nuclear fission", "Similar to nuclear reactors"]
* FN: \["Powered by nuclear fusion", "Hydrogen fuses to form helium"]
* F1 Score: 0.20 → ❌ Fail
### Score Examples
| TP | FP | FN | F1 Score | Result | Notes |
| -- | -- | -- | -------- | ------ | ------------------------- |
| 5 | 0 | 0 | 1.0 | ✅ Pass | Perfect accuracy |
| 5 | 0 | 1 | 0.91 | ✅ Pass | Minor omission acceptable |
| 5 | 1 | 0 | 0.91 | ✅ Pass | Minor error acceptable |
| 4 | 1 | 0 | 0.8 | ✅ Pass | Boundary case |
| 3 | 0 | 2 | 0.75 | ❌ Fail | Too many omissions |
| 1 | 4 | 0 | 0.33 | ❌ Fail | Mostly incorrect |
### When to Use
* Financial data and calculations
* Medical or legal information
* Product specifications and features
* Any domain where factual accuracy is critical
## Custom
Create domain-specific evaluations for your unique business requirements.
### What It Evaluates
Whatever you define in a custom criterion. Common use cases:
* Regulatory compliance checks
* Schema or format validation
* Latency or performance SLAs
* Business logic requirements
* Security and privacy rules
### How It Works
You provide a criterion describing what to check. An LLM evaluates the response and returns:
* Binary pass/fail (1 or 0)
* Reasoning explaining the decision
**Pass Criteria:**
* Score = 1 (criterion met)
### Example Criteria
```markdown theme={null}
# Compliance Example
"The response must not mention specific account numbers,
social security numbers, or other PII. Pass if no PII is present."
# Format Example
"The response must be formatted as a JSON object with
'action', 'parameters', and 'reasoning' keys. Pass if valid JSON
with all required keys."
# Business Logic Example
"For loan inquiries, the response must ask for income verification
before discussing loan amounts. Pass if verification is requested first."
# Chatbot Boundaries Example
"When asked to perform actions outside the chatbot's scope (e.g.,
processing refunds, accessing user accounts, making reservations),
the response must politely decline and explain limitations. Pass if
the chatbot appropriately refuses and provides alternative guidance."
```
### When to Use
* Industry-specific compliance requirements
* Custom business rules and workflows
* Structured output validation
* Security and privacy checks
* Chatbot safety and boundaries
* Any evaluation not covered by built-in types
## Best Practices
### Combining Evaluations
Use multiple evaluation types together for comprehensive quality assurance. The right combination depends on what your specific task does:
* **Knowledge Base Q\&A (RAG):** Recall + Fact Checker + Naturalness
* **Creative Content Generation:** Naturalness + Style + Fact Checker (if accuracy matters)
* **Retrieval-Based Customer Support:** Recall + Naturalness + Style + Custom (compliance)
* **Direct Response (no retrieval):** Naturalness + Style + Custom (compliance)
* **Chatbot with Boundaries:** Naturalness + Custom (safety/boundaries) + Custom (compliance)
* **Structured Output:** Custom (format) + Custom (business logic)
Choose evaluations based on your task's behavior, not just your application type. For example, a customer support application might use different evaluation combinations for retrieval-based responses versus direct answers, and might add Custom evaluations to ensure the chatbot properly refuses out-of-scope requests.
## Issue Creation
When an evaluation fails, Avido automatically creates an issue with:
* **Title** – Evaluation type and failure summary
* **Priority** – HIGH, MEDIUM, or LOW based on severity
* **Description** – Scores, reasoning, and context
* **Trace Link** – Direct access to the full conversation
All issues appear in your [Inbox](/inbox) for triage and resolution.
## Need Help?
* **Email** – [support@avidoai.com](mailto:support@avidoai.com)
For API details and integration guides, see the [API Reference](/api-reference).
# Inbox
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/inbox
Central hub for triaging and managing all AI application issues and regressions
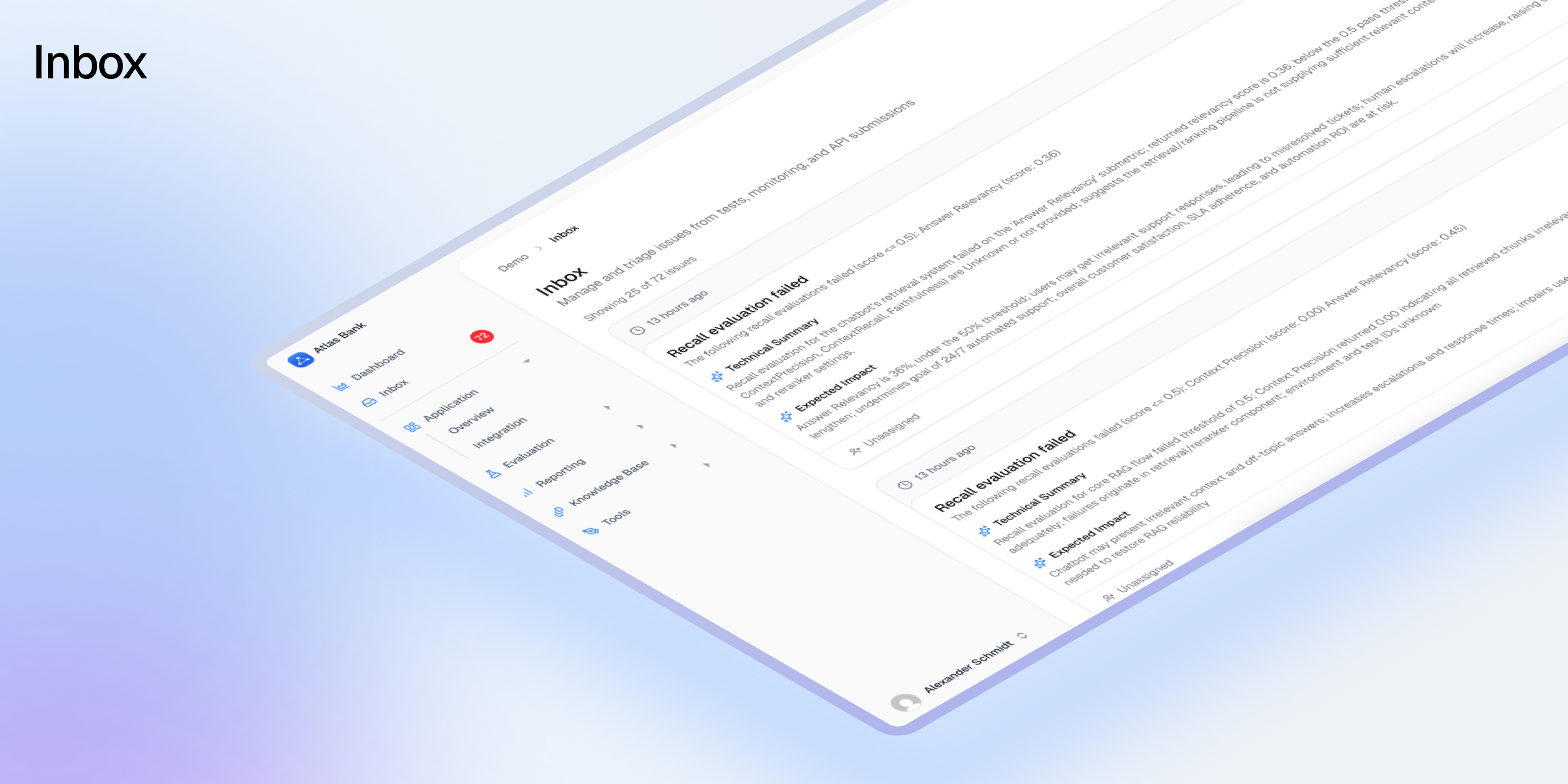
The Avido Inbox is where all issues and regressions in your AI application are gathered, triaged, and assigned. With the Inbox, you know where to start your day, and what issues to tackle first. It also allows for smooth and frictionless collaboration between stakeholders. A response is flagged as providing wrong answers? Assign it to the document owner. An answer about a feature is vague or contradictory? Assign the product manager who can clear it up. Technical error? Route it to the dev in charge.
An AI application is never done, nor perfect. It's a continuous cycle of improvement through collaboration. This is what the Inbox solves.
## What is the Inbox?
The Inbox is a real-time, multi-source queue for all high-priority platform issues. It consolidates test failures, System Journal alerts, customer reports, and API-submitted errors into a single, actionable queue. Every incoming item is automatically summarized, categorized, and prioritized before surfacing to users, who can rapidly triage and assign.
This is a focused, high-signal triage and assignment tool—not a deep workbench or collaborative analysis surface. It's designed to help you quickly understand what's wrong and get it to the right person.
## Issues
Issues are the core of the Inbox. Every regression, bug, potential hallucination, or actual error is processed and added into the Inbox as an issue.
### When Issues Appear
Issues show up when:
* **A test run by Avido fails**: Evaluation tests that don't meet their thresholds automatically create issues
* **System Journal entries flag critical changes**: Configuration changes outside acceptable ranges trigger issues
* **External API submissions**: Your application or third-party services call the Avido `/issues` endpoint
* **Future**: Customer reports and AI Core alerts (planned)
Before getting added to the Inbox, Avido's AI pre-processes each issue to make it actionable for your entire team.
### Pre-Processing Pipeline
One of the core benefits of using Avido is the ability to work from the same truth, even when some stakeholders are technical, like engineers, and some are non-technical like SMEs. To enable this, Avido pre-processes all incoming issues before adding them to the Inbox.
During processing, Avido's AI will:
* **Summarize the issue**: Create both business and technical summaries
* **Estimate impact**: Assess the expected effect this issue will have
* **Assign priority**: Set criticality level (Critical, High, Medium, Low)
* **Find similar issues**: Detect duplicates and related problems using AI embeddings
* **Add metadata**: Include source, timestamps, and relevant context
This allows you to focus on the errors that matter most and keeps everyone working from the same truth about what's happening and how it's affecting the application. Less coordination, faster time-to-fix.
## Using the Inbox
### Accessing Your Inbox
Navigate to the **Inbox** section in your Avido dashboard. You'll see a real-time queue of all unresolved issues, sorted by priority and creation time.
### Understanding Issue Cards
Each issue displays:
* **Priority Badge**: Visual indicator of criticality
* **Source**: Where the issue originated (Test, System Journal, API)
* **Title**: Clear description of the problem
* **Business Summary**: Plain-language explanation (default view)
* **Technical Summary**: Detailed technical context (toggle to view)
* **Metadata**: Creation time, affected systems, related traces
* **Similar Issues**: Count of potentially related problems
### Core Actions
#### Triage Workflow
1. **Review**: Scan the queue, starting with highest priority items
2. **Understand**: Read AI-generated summaries to grasp impact
3. **Act**: Take one of these actions:
* **Assign**: Route to a specific user or team with optional notes
* **Dismiss**: Mark as resolved or non-actionable with a reason
* **Merge**: Combine with similar issues to reduce duplication
#### Bulk Operations
Select multiple issues using checkboxes to:
* Assign all to one person
* Dismiss multiple non-issues
* Apply the same action to related problems
### Business vs Technical Views
Every issue comes with two perspectives:
* **Business Summary** (default): What happened and why it matters, in plain English
* **Technical Summary**: Root cause details, stack traces, and technical context
Toggle between views based on your needs and audience.
## The Issues API
The `/issues` endpoint allows you to create issues and send them straight into the Avido Inbox from any application.
### Example Use Cases
* **Catch technical errors**: Send application errors directly to the Inbox
* **User feedback**: Allow users to report hallucinations or unhelpful answers
* **Support integration**: Let customer service reps create issues from support tools
### API Usage
```bash theme={null}
POST /v0/issues
Authorization: Bearer YOUR_API_KEY
Content-Type: application/json
{
"title": "User reported incorrect product pricing",
"description": "AI provided outdated pricing information",
"priority": "HIGH",
"metadata": {
"conversation_id": "conv_123",
"affected_product": "premium_plan"
}
}
```
Issues sent via the API go through the same pre-processing pipeline as any issue that Avido creates. Include as much context as possible for better summarization and categorization.
**Important**: Always PII-scrub any personal information before sending to the API.
## Deduplication & Similar Issues
The Inbox uses AI embeddings to automatically detect similar issues:
* **Automatic Detection**: Flags potential duplicates with similarity percentages
* **Merge Suggestions**: Recommends combining highly similar issues (>90% similarity)
* **Pattern Recognition**: Groups related issues to reveal systemic problems
This prevents alert fatigue and helps you see the bigger picture when multiple related issues occur.
## Best Practices
### Daily Triage
* Start your day by reviewing new issues in the Inbox
* Focus on High priority items first
* Aim for "Inbox Zero" - clearing all unassigned urgent issues
### Effective Assignment
* Assign based on expertise and current workload
* Add notes when assigning to provide context
* Reassign if someone is overwhelmed
### Maintain Inbox Hygiene
* Dismiss false positives promptly with clear reasons
* Merge duplicates to keep the inbox clean
* Don't let issues accumulate - triage regularly
### Leverage AI Summaries
* Use business summaries for quick understanding
* Switch to technical view when diving into implementation
* Trust the AI prioritization but apply your judgment
## Success Metrics
The Inbox helps you track:
* **Response Time**: How quickly issues are triaged and assigned
* **Resolution Rate**: Percentage of issues successfully resolved
* **False Positive Rate**: How many dismissed issues were non-actionable
* **Pattern Detection**: Recurring issues that indicate systemic problems
## Current Limitations
The Inbox is designed as a triage tool, not a full incident management platform:
* No multi-step workflows or root-cause analysis features
* No deep collaboration workspaces within the Inbox
* Limited to standardized `/issues` API for external submissions
## Getting Started
1. **Automatic Setup**: The Inbox is ready to use immediately
2. **First Issues**: Will appear as soon as tests fail or issues are submitted
3. **Customization**: Contact your Avido team to adjust priority thresholds or configure integrations
The Inbox transforms issue management from scattered alerts across multiple systems into a single source of truth, ensuring your team addresses what matters most and nothing falls through the cracks.
# Welcome to Avido Docs 🚀
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/introduction
The AI Quality Assurance platform built for fintechs and financial services enterprises.
## Why Avido?
Only 10% of financial enterprises have AI in full production. Avido changes that by providing the quality safety net your AI needs.
* **Evaluation & Testing** – Simulate user interactions to rigorously test AI systems before and after deployment
* **Continuous Monitoring** – Track safety, accuracy, and performance in live production environments
* **Collaborative Tools** – SMEs and developers work together through an intuitive GUI – no coding required for domain experts
* **Compliance-First** – Built for GDPR, EU AI Act with audit trails and standardized QA processes
* **Automated System Journal** – Detect configuration changes automatically and prevent hidden regressions
* **Quickstart** – Upload existing conversations to auto-generate test cases and evaluation criteria
* **Documents** – AI-optimized knowledge management with version control and approval workflows
Whether you're building a support assistant, an autonomous agent, or a RAG pipeline, Avido ensures your AI performs safely, accurately, and in compliance from launch through ongoing operations.
***
## How Avido fits into your app
We're thrilled to share our first public changelog, marking a step forward in our commitment to enhancing the understanding of AI applications and helping enterprises maximize the value of AI with Avido.
### 🚀 Quickstart Workflow
* Upload existing outputs via CSV to automatically generate evaluation cases
* Smart AI-powered categorization of topics and tasks
* Interactive review interface for selecting benchmark outputs
* Automated evaluation criteria generation based on selected examples
### 📊 Improved Scoring System
* Simplified scoring scale (1-5) for more intuitive evaluation
* Updated benchmarking system for better quality assessment
* Refined evaluation criteria for clearer quality metrics
### 🤖 Smart Analysis
* Automatic topic detection from output patterns
* Task identification based on user intentions
* Intelligent grouping of similar outputs
* Automated quality scoring of historical outputs
### 💡 Enhanced Review Experience
* Visual topic distribution analysis
* Side-by-side conversation comparison
* Guided selection of benchmark outputs
* Contextual feedback collection for evaluation criteria
# Documents
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/documents
Knowledge management system for creating, versioning, and optimizing RAG-ready content

The Documents tool allows you to easily format and split your content into RAG-ready documents. It's your central knowledge base where teams can collaborate on creating, refining, and approving the content that powers your AI application. Whether you're building customer support bots, internal knowledge assistants, or any RAG-based system, Documents ensures your content is properly structured, versioned, and optimized for AI retrieval.
## What are Documents?
Documents in Avido are structured content pieces designed specifically for Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems. Unlike traditional document management, Avido Documents are:
* **AI-Optimized**: Automatically chunked and formatted for optimal retrieval
* **Version-Controlled**: Maintain approved versions in production while working on improvements
* **Collaborative**: Multiple team members can work on drafts without affecting live content
* **Traceable**: Every change is tracked for compliance and quality control
## Key Features
### Document Creation & Import
Documents can be created in multiple ways:
* **Manual Creation**: Write and format content directly in the Avido editor
* **Web Scraping**: Import content from any public URL
* **File Upload**: Upload existing documents (coming soon)
* **API Integration**: Programmatically create and manage documents
### AI-Powered Optimization
The platform includes intelligent document optimization that:
* **Reformats for RAG**: Structures content for better chunking and retrieval
* **Improves Clarity**: Enhances readability while preserving meaning
* **Maintains Consistency**: Ensures uniform formatting across your knowledge base
* **Preserves Intent**: Keeps the original message and tone intact
### Version Management
Every document supports comprehensive versioning:
#### Version States
* **APPROVED**: Live production version served by APIs
* **DRAFT**: Work-in-progress version for collaboration
* **REVIEW**: Pending approval from designated reviewers
* **ARCHIVED**: Historical versions for reference
#### Version Workflow
1. Create new versions from any existing version
2. Collaborate on drafts without affecting production
3. Submit for review when ready
4. Approve to make it the live version
5. Previous approved versions are automatically archived
### Approval Workflow
Documents can require approval before going live:
* **Assign Reviewers**: Designate who needs to approve changes
* **Email Notifications**: Reviewers are notified when approval is needed
* **Audit Trail**: Track who approved what and when
* **Compliance Ready**: Meet regulatory requirements for content control
## Using Documents
### Creating Your First Document
1. Navigate to the **Documents** section in your Avido dashboard
2. Click **New Document**
3. Choose your creation method:
* **Write**: Start with the built-in editor
* **Import from URL**: Scrape content from a website
* **Upload**: Import existing files (if enabled)
### Document Editor
The editor provides a rich set of formatting tools:
* **Markdown Support**: Write in markdown for quick formatting
* **Visual Editor**: Use the toolbar for formatting without markdown knowledge
* **Preview Mode**: See how your document will appear to users
* **Auto-Save**: Never lose your work with automatic saving
### Working with Versions
#### Creating a New Version
1. Open any document
2. Click **Create New Version** in the version sidebar
3. Add version notes describing your changes
4. Edit the content as needed
5. Save as draft or submit for review
#### Version History Sidebar
The sidebar shows:
* All versions with their status badges
* Creator and approval information
* Version notes and timestamps
* Quick actions for each version
#### Comparing Versions
1. Select two versions to compare
2. View side-by-side differences
3. See what was added, removed, or changed
4. Understand the evolution of your content
### Document Optimization
Use AI to improve your documents:
1. Open any document
2. Click **Optimize Document**
3. Review the AI-suggested improvements
4. Accept, reject, or modify suggestions
5. Save the optimized version
The optimizer helps with:
* Breaking content into logical sections
* Improving readability and clarity
* Standardizing formatting
* Enhancing retrieval effectiveness
### API Access
Documents are accessible via the Avido API:
```bash theme={null}
# Get all approved documents
GET /v0/documents
Authorization: Bearer YOUR_API_KEY
# Get a specific document
GET /v0/documents/{id}
# Include draft versions
GET /v0/documents?include_drafts=true
# Create a new document
POST /v0/documents
Content-Type: application/json
{
"title": "Product FAQ",
"content": "# Frequently Asked Questions...",
"metadata": {
"category": "support",
"product": "main"
}
}
```
### Integration with Testing
Documents integrate seamlessly with Avido's testing framework:
* **Knowledge Coverage**: Test if your documents cover all required topics
* **MECE Analysis**: Ensure content is Mutually Exclusive and Collectively Exhaustive
* **Task Mapping**: Verify documents address all user tasks
Tests automatically use approved versions unless configured otherwise.
## Best Practices
### Content Organization
* **Use Clear Titles**: Make documents easily discoverable
* **Add Metadata**: Tag documents with categories, products, or teams
* **Structure Hierarchically**: Use headings to create logical sections
* **Keep Focused**: One topic per document for better retrieval
### Version Management
* **Document Changes**: Always add clear version notes
* **Review Before Approval**: Have subject matter experts review changes
* **Test Before Production**: Run coverage tests on new versions
* **Archive Strategically**: Keep important historical versions accessible
### Collaboration
* **Assign Ownership**: Each document should have a clear owner
* **Use Draft Status**: Work on improvements without affecting production
* **Communicate Changes**: Notify stakeholders of significant updates
* **Regular Reviews**: Schedule periodic content audits
### RAG Optimization
* **Chunk-Friendly Content**: Write in digestible sections
* **Avoid Redundancy**: Don't duplicate information across documents
* **Use Examples**: Include concrete examples for better context
* **Update Regularly**: Keep content current and accurate
## Document Lifecycle
### 1. Creation Phase
* Identify knowledge gaps
* Create initial content
* Format for readability
* Add relevant metadata
### 2. Optimization Phase
* Run AI optimization
* Test with knowledge coverage
* Refine based on feedback
* Ensure completeness
### 3. Review Phase
* Submit for approval
* Gather stakeholder feedback
* Make necessary revisions
* Document decisions
### 4. Production Phase
* Approve for production use
* Monitor retrieval performance
* Track usage in traces
* Gather user feedback
### 5. Maintenance Phase
* Regular content audits
* Update outdated information
* Create new versions as needed
* Archive obsolete content
## Advanced Features
### Traceability
When documents are used in AI responses, Avido tracks:
* Which documents were retrieved
* How they influenced the response
This creates a feedback loop for continuous improvement.
## Getting Started
1. **Define Your Knowledge Base**: Identify what content your AI needs
2. **Create Initial Documents**: Start with your most critical content
3. **Optimize and Test**: Use AI optimization and run coverage tests
4. **Review and Approve**: Get stakeholder sign-off
5. **Monitor and Iterate**: Track usage and improve based on feedback
Documents transform static knowledge into dynamic, AI-ready content that evolves with your application's needs, ensuring your AI always has access to accurate, approved, and optimized information.
# Evaluations
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/evaluations
Built-in and custom evaluation types to measure AI quality, safety, and performance.
## Overview
Avido provides six evaluation types to measure different aspects of AI quality. Each evaluation is applied to tasks, then runs automatically when those tasks execute, providing actionable insights when quality standards aren't met.
| Evaluation Type | Purpose | Score Range | Pass Threshold |
| ---------------- | -------------------------------- | ----------- | -------------- |
| **Naturalness** | Human-like communication quality | 1-5 | 3.5 |
| **Style** | Brand guideline compliance | 1-5 | 3.5 |
| **Recall** | RAG pipeline performance | 0-1 | 0.5 |
| **Fact Checker** | Factual accuracy vs ground truth | 0-1 | 0.8 |
| **Custom** | Domain-specific criteria | 0-1 | 0.5 |
## Naturalness
Measures how natural, engaging, and clear your AI's responses are to users.
### What It Evaluates
The Naturalness evaluation assesses five dimensions of response quality:
* **Coherence** – Logical flow and consistency of ideas
* **Engagingness** – Ability to capture and maintain user interest
* **Naturalness** – Human-like language and tone
* **Relevance** – On-topic responses that address the user's intent
* **Clarity** – Clear, understandable language without ambiguity
### How It Works
An LLM evaluates your AI's response across all five dimensions on a 1-5 scale. The overall score is the average of these dimensions.
**Pass Criteria:**
* All five dimensions must score ≥ 3.5
* Average score ≥ 3.5
This ensures no single dimension fails even if the overall average is high.
### Example Results
| Coherence | Engagingness | Naturalness | Relevance | Clarity | Overall | Result |
| --------- | ------------ | ----------- | --------- | ------- | ------- | ----------------------- |
| 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5.0 | ✅ Pass |
| 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4.0 | ✅ Pass |
| 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 2 | 4.4 | ❌ Fail (Clarity \< 3.5) |
### When to Use
* Conversational AI and chatbots
* Customer support automation
* Content generation systems
* Any user-facing AI interactions
## Style
Evaluates whether responses adhere to your organization's style guidelines and brand voice.
### What It Evaluates
A single comprehensive score (1-5) based on your custom style guide, measuring:
* Tone and voice consistency
* Terminology usage
* Format and structure requirements
* Brand-specific guidelines
* Reading level and complexity
### How It Works
You provide a style guide document that defines your brand's communication standards. An LLM evaluates each response against this guide and provides:
* A score from 1-5
* Detailed analysis explaining the rating
**Pass Criteria:**
* Score ≥ 3.5
### Example Style Guide Elements
```markdown theme={null}
# Customer Support Style Guide
**Tone:** Professional yet friendly, never casual
**Voice:** Active voice preferred, clear and direct
**Terminology:** Use "account" not "profile", "transfer" not "send"
**Format:** Start with acknowledgment, provide solution, end with offer to help
**Constraints:** Keep responses under 100 words when possible
```
### When to Use
* Brand-critical communications
* Multi-channel consistency (chat, email, voice)
* Customer-facing applications where brand matters
Note: For regulated industries with strict compliance requirements, use Custom evaluations instead.
## Recall (RAG Evaluation)
Comprehensive evaluation of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) pipeline quality.
### What It Evaluates
Four metrics that measure different aspects of RAG performance:
* **Context Relevancy** – Are retrieved documents relevant to the query?
* **Context Precision** – How well-ranked are the retrieved documents?
* **Faithfulness** – Is the answer grounded in the retrieved context?
* **Answer Relevancy** – Does the answer address the user's question?
### How It Works
Each metric produces a score from 0-1 (higher is better). The overall score is the average of Context Precision, Faithfulness, and Answer Relevancy.
**Pass Criteria:**
* Context Precision ≥ 0.5
* Faithfulness ≥ 0.5
* Answer Relevancy ≥ 0.5
Note: Context Relevancy is computed for observability but doesn't affect pass/fail status.
### Score Interpretation
| Score Range | Interpretation | Action Required |
| ----------- | --------------------- | ----------------------- |
| 0.8 - 1.0 | Excellent performance | Monitor |
| 0.5 - 0.8 | Acceptable quality | Optimize if critical |
| 0.0 - 0.5 | Poor performance | Investigate immediately |
### Common Issues and Solutions
| Low Metric | Likely Cause | Solution |
| ----------------- | ------------------------------------ | ---------------------------------------------- |
| Context Precision | Too many irrelevant chunks retrieved | Reduce top\_k, improve filters |
| Context Relevancy | Embedding/index drift | Retrain embeddings, update index |
| Faithfulness | Model hallucinating | Add grounding instructions, reduce temperature |
| Answer Relevancy | Answer drifts off-topic | Improve prompt focus, add constraints |
### When to Use
* Knowledge base search and retrieval
* Document Q\&A systems
* RAG pipelines
* Any system combining retrieval with generation
## Fact Checker
Validates factual accuracy of AI responses against ground truth.
### What It Evaluates
Compares AI-generated statements with known correct information, classifying each statement as:
* **True Positives (TP)** – Correct facts present in the response
* **False Positives (FP)** – Incorrect facts in the response
* **False Negatives (FN)** – Correct facts omitted from the response
### How It Works
An LLM extracts factual statements from both the AI response and ground truth, then classifies them. The F1 score measures accuracy:
```
F1 = TP / (TP + 0.5 × (FP + FN))
```
**Pass Criteria:**
* F1 score ≥ 0.8
This allows high-quality answers with minor omissions while maintaining strict accuracy standards.
### Example Classification
**Question:** "What powers the sun?"
**Ground Truth:** "The sun is powered by nuclear fusion. In its core, hydrogen atoms fuse to form helium, releasing tremendous energy."
**AI Response:** "The sun is powered by nuclear fission, similar to nuclear reactors, and provides light to the solar system."
**Classification:**
* TP: \["Provides light to the solar system"]
* FP: \["Powered by nuclear fission", "Similar to nuclear reactors"]
* FN: \["Powered by nuclear fusion", "Hydrogen fuses to form helium"]
* F1 Score: 0.20 → ❌ Fail
### Score Examples
| TP | FP | FN | F1 Score | Result | Notes |
| -- | -- | -- | -------- | ------ | ------------------------- |
| 5 | 0 | 0 | 1.0 | ✅ Pass | Perfect accuracy |
| 5 | 0 | 1 | 0.91 | ✅ Pass | Minor omission acceptable |
| 5 | 1 | 0 | 0.91 | ✅ Pass | Minor error acceptable |
| 4 | 1 | 0 | 0.8 | ✅ Pass | Boundary case |
| 3 | 0 | 2 | 0.75 | ❌ Fail | Too many omissions |
| 1 | 4 | 0 | 0.33 | ❌ Fail | Mostly incorrect |
### When to Use
* Financial data and calculations
* Medical or legal information
* Product specifications and features
* Any domain where factual accuracy is critical
## Custom
Create domain-specific evaluations for your unique business requirements.
### What It Evaluates
Whatever you define in a custom criterion. Common use cases:
* Regulatory compliance checks
* Schema or format validation
* Latency or performance SLAs
* Business logic requirements
* Security and privacy rules
### How It Works
You provide a criterion describing what to check. An LLM evaluates the response and returns:
* Binary pass/fail (1 or 0)
* Reasoning explaining the decision
**Pass Criteria:**
* Score = 1 (criterion met)
### Example Criteria
```markdown theme={null}
# Compliance Example
"The response must not mention specific account numbers,
social security numbers, or other PII. Pass if no PII is present."
# Format Example
"The response must be formatted as a JSON object with
'action', 'parameters', and 'reasoning' keys. Pass if valid JSON
with all required keys."
# Business Logic Example
"For loan inquiries, the response must ask for income verification
before discussing loan amounts. Pass if verification is requested first."
# Chatbot Boundaries Example
"When asked to perform actions outside the chatbot's scope (e.g.,
processing refunds, accessing user accounts, making reservations),
the response must politely decline and explain limitations. Pass if
the chatbot appropriately refuses and provides alternative guidance."
```
### When to Use
* Industry-specific compliance requirements
* Custom business rules and workflows
* Structured output validation
* Security and privacy checks
* Chatbot safety and boundaries
* Any evaluation not covered by built-in types
## Best Practices
### Combining Evaluations
Use multiple evaluation types together for comprehensive quality assurance. The right combination depends on what your specific task does:
* **Knowledge Base Q\&A (RAG):** Recall + Fact Checker + Naturalness
* **Creative Content Generation:** Naturalness + Style + Fact Checker (if accuracy matters)
* **Retrieval-Based Customer Support:** Recall + Naturalness + Style + Custom (compliance)
* **Direct Response (no retrieval):** Naturalness + Style + Custom (compliance)
* **Chatbot with Boundaries:** Naturalness + Custom (safety/boundaries) + Custom (compliance)
* **Structured Output:** Custom (format) + Custom (business logic)
Choose evaluations based on your task's behavior, not just your application type. For example, a customer support application might use different evaluation combinations for retrieval-based responses versus direct answers, and might add Custom evaluations to ensure the chatbot properly refuses out-of-scope requests.
## Issue Creation
When an evaluation fails, Avido automatically creates an issue with:
* **Title** – Evaluation type and failure summary
* **Priority** – HIGH, MEDIUM, or LOW based on severity
* **Description** – Scores, reasoning, and context
* **Trace Link** – Direct access to the full conversation
All issues appear in your [Inbox](/inbox) for triage and resolution.
## Need Help?
* **Email** – [support@avidoai.com](mailto:support@avidoai.com)
For API details and integration guides, see the [API Reference](/api-reference).
# Inbox
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/inbox
Central hub for triaging and managing all AI application issues and regressions

The Avido Inbox is where all issues and regressions in your AI application are gathered, triaged, and assigned. With the Inbox, you know where to start your day, and what issues to tackle first. It also allows for smooth and frictionless collaboration between stakeholders. A response is flagged as providing wrong answers? Assign it to the document owner. An answer about a feature is vague or contradictory? Assign the product manager who can clear it up. Technical error? Route it to the dev in charge.
An AI application is never done, nor perfect. It's a continuous cycle of improvement through collaboration. This is what the Inbox solves.
## What is the Inbox?
The Inbox is a real-time, multi-source queue for all high-priority platform issues. It consolidates test failures, System Journal alerts, customer reports, and API-submitted errors into a single, actionable queue. Every incoming item is automatically summarized, categorized, and prioritized before surfacing to users, who can rapidly triage and assign.
This is a focused, high-signal triage and assignment tool—not a deep workbench or collaborative analysis surface. It's designed to help you quickly understand what's wrong and get it to the right person.
## Issues
Issues are the core of the Inbox. Every regression, bug, potential hallucination, or actual error is processed and added into the Inbox as an issue.
### When Issues Appear
Issues show up when:
* **A test run by Avido fails**: Evaluation tests that don't meet their thresholds automatically create issues
* **System Journal entries flag critical changes**: Configuration changes outside acceptable ranges trigger issues
* **External API submissions**: Your application or third-party services call the Avido `/issues` endpoint
* **Future**: Customer reports and AI Core alerts (planned)
Before getting added to the Inbox, Avido's AI pre-processes each issue to make it actionable for your entire team.
### Pre-Processing Pipeline
One of the core benefits of using Avido is the ability to work from the same truth, even when some stakeholders are technical, like engineers, and some are non-technical like SMEs. To enable this, Avido pre-processes all incoming issues before adding them to the Inbox.
During processing, Avido's AI will:
* **Summarize the issue**: Create both business and technical summaries
* **Estimate impact**: Assess the expected effect this issue will have
* **Assign priority**: Set criticality level (Critical, High, Medium, Low)
* **Find similar issues**: Detect duplicates and related problems using AI embeddings
* **Add metadata**: Include source, timestamps, and relevant context
This allows you to focus on the errors that matter most and keeps everyone working from the same truth about what's happening and how it's affecting the application. Less coordination, faster time-to-fix.
## Using the Inbox
### Accessing Your Inbox
Navigate to the **Inbox** section in your Avido dashboard. You'll see a real-time queue of all unresolved issues, sorted by priority and creation time.
### Understanding Issue Cards
Each issue displays:
* **Priority Badge**: Visual indicator of criticality
* **Source**: Where the issue originated (Test, System Journal, API)
* **Title**: Clear description of the problem
* **Business Summary**: Plain-language explanation (default view)
* **Technical Summary**: Detailed technical context (toggle to view)
* **Metadata**: Creation time, affected systems, related traces
* **Similar Issues**: Count of potentially related problems
### Core Actions
#### Triage Workflow
1. **Review**: Scan the queue, starting with highest priority items
2. **Understand**: Read AI-generated summaries to grasp impact
3. **Act**: Take one of these actions:
* **Assign**: Route to a specific user or team with optional notes
* **Dismiss**: Mark as resolved or non-actionable with a reason
* **Merge**: Combine with similar issues to reduce duplication
#### Bulk Operations
Select multiple issues using checkboxes to:
* Assign all to one person
* Dismiss multiple non-issues
* Apply the same action to related problems
### Business vs Technical Views
Every issue comes with two perspectives:
* **Business Summary** (default): What happened and why it matters, in plain English
* **Technical Summary**: Root cause details, stack traces, and technical context
Toggle between views based on your needs and audience.
## The Issues API
The `/issues` endpoint allows you to create issues and send them straight into the Avido Inbox from any application.
### Example Use Cases
* **Catch technical errors**: Send application errors directly to the Inbox
* **User feedback**: Allow users to report hallucinations or unhelpful answers
* **Support integration**: Let customer service reps create issues from support tools
### API Usage
```bash theme={null}
POST /v0/issues
Authorization: Bearer YOUR_API_KEY
Content-Type: application/json
{
"title": "User reported incorrect product pricing",
"description": "AI provided outdated pricing information",
"priority": "HIGH",
"metadata": {
"conversation_id": "conv_123",
"affected_product": "premium_plan"
}
}
```
Issues sent via the API go through the same pre-processing pipeline as any issue that Avido creates. Include as much context as possible for better summarization and categorization.
**Important**: Always PII-scrub any personal information before sending to the API.
## Deduplication & Similar Issues
The Inbox uses AI embeddings to automatically detect similar issues:
* **Automatic Detection**: Flags potential duplicates with similarity percentages
* **Merge Suggestions**: Recommends combining highly similar issues (>90% similarity)
* **Pattern Recognition**: Groups related issues to reveal systemic problems
This prevents alert fatigue and helps you see the bigger picture when multiple related issues occur.
## Best Practices
### Daily Triage
* Start your day by reviewing new issues in the Inbox
* Focus on High priority items first
* Aim for "Inbox Zero" - clearing all unassigned urgent issues
### Effective Assignment
* Assign based on expertise and current workload
* Add notes when assigning to provide context
* Reassign if someone is overwhelmed
### Maintain Inbox Hygiene
* Dismiss false positives promptly with clear reasons
* Merge duplicates to keep the inbox clean
* Don't let issues accumulate - triage regularly
### Leverage AI Summaries
* Use business summaries for quick understanding
* Switch to technical view when diving into implementation
* Trust the AI prioritization but apply your judgment
## Success Metrics
The Inbox helps you track:
* **Response Time**: How quickly issues are triaged and assigned
* **Resolution Rate**: Percentage of issues successfully resolved
* **False Positive Rate**: How many dismissed issues were non-actionable
* **Pattern Detection**: Recurring issues that indicate systemic problems
## Current Limitations
The Inbox is designed as a triage tool, not a full incident management platform:
* No multi-step workflows or root-cause analysis features
* No deep collaboration workspaces within the Inbox
* Limited to standardized `/issues` API for external submissions
## Getting Started
1. **Automatic Setup**: The Inbox is ready to use immediately
2. **First Issues**: Will appear as soon as tests fail or issues are submitted
3. **Customization**: Contact your Avido team to adjust priority thresholds or configure integrations
The Inbox transforms issue management from scattered alerts across multiple systems into a single source of truth, ensuring your team addresses what matters most and nothing falls through the cracks.
# Welcome to Avido Docs 🚀
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/introduction
The AI Quality Assurance platform built for fintechs and financial services enterprises.
## Why Avido?
Only 10% of financial enterprises have AI in full production. Avido changes that by providing the quality safety net your AI needs.
* **Evaluation & Testing** – Simulate user interactions to rigorously test AI systems before and after deployment
* **Continuous Monitoring** – Track safety, accuracy, and performance in live production environments
* **Collaborative Tools** – SMEs and developers work together through an intuitive GUI – no coding required for domain experts
* **Compliance-First** – Built for GDPR, EU AI Act with audit trails and standardized QA processes
* **Automated System Journal** – Detect configuration changes automatically and prevent hidden regressions
* **Quickstart** – Upload existing conversations to auto-generate test cases and evaluation criteria
* **Documents** – AI-optimized knowledge management with version control and approval workflows
Whether you're building a support assistant, an autonomous agent, or a RAG pipeline, Avido ensures your AI performs safely, accurately, and in compliance from launch through ongoing operations.
***
## How Avido fits into your app
![Diagram showing how Avido fits into your app]() 1. **Avido sends a webhook** – When a test is triggered, Avido sends a POST request to your endpoint with synthetic input and a testId.
2. **You validate the request** – Verify the webhook signature to ensure it's really from Avido.
3. **Run your AI workflow** – Process the synthetic input through your normal application flow.
4. **Log events along the way** – Capture LLM calls, tool usage, retrievals, and other key steps.
5. **Send the trace to Avido** – When your workflow completes, send the full event trace back to Avido.
6. **View evaluation results** – Avido runs your configured evaluations and displays results in the dashboard.
***
## Getting Started
1. **Install an SDK**
```bash theme={null}
npm i @avidoai/sdk-node # Node
pip install avido # Python
```
2. **Setup a webhook endpoint** in your application [Learn more](/webhooks)
3. **Start tracing events** in your application [Learn more](/traces)
4. **Create your knowledge base** with Documents [Learn more](/documents)
```ts theme={null}
client.ingest.create({ events })
```
5. **Upload existing data** to auto-generate test cases and evaluations [Learn more](/quickstart)
6. **Review your baseline performance** in the dashboard
> Prefer pure HTTP? All endpoints are [documented here](/api-reference).
***
## Core concepts
| Concept | TL;DR |
| ------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| **Tests** | Automated runs of your workflow using synthetic input without exposing customer data. |
| **Tasks** | Test cases that can be auto-generated from existing data or created manually. |
| **Webhooks** | Avido triggers tests via POST requests – automated or through the UI. |
| **Traces** | Ordered lists of events that reconstruct a conversation / agent run. |
| **Events** | Atomic pieces of work (`llm`, `tool`, `retriever`, `log`). |
| **Evaluations** | Built-in metrics + custom business logic tests created without code. |
| **Documents** | Version-controlled, RAG-ready content that powers your AI's knowledge base. |
| **Inbox** | Central hub where all issues are captured, summarized, and triaged automatically. |
| **System Journal** | Automatic log of configuration changes and their impact on performance. |
Dive deeper with the sidebar or jump straight to **[Traces](/traces)** to see how instrumentation works.
***
## Need help?
* **Email** – [support@avidoai.com](mailto:support@avidoai.com)
Happy building! ✨
# System Journal
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/system-journal
Automated monitoring and documentation of AI model changes for compliance and operational excellence
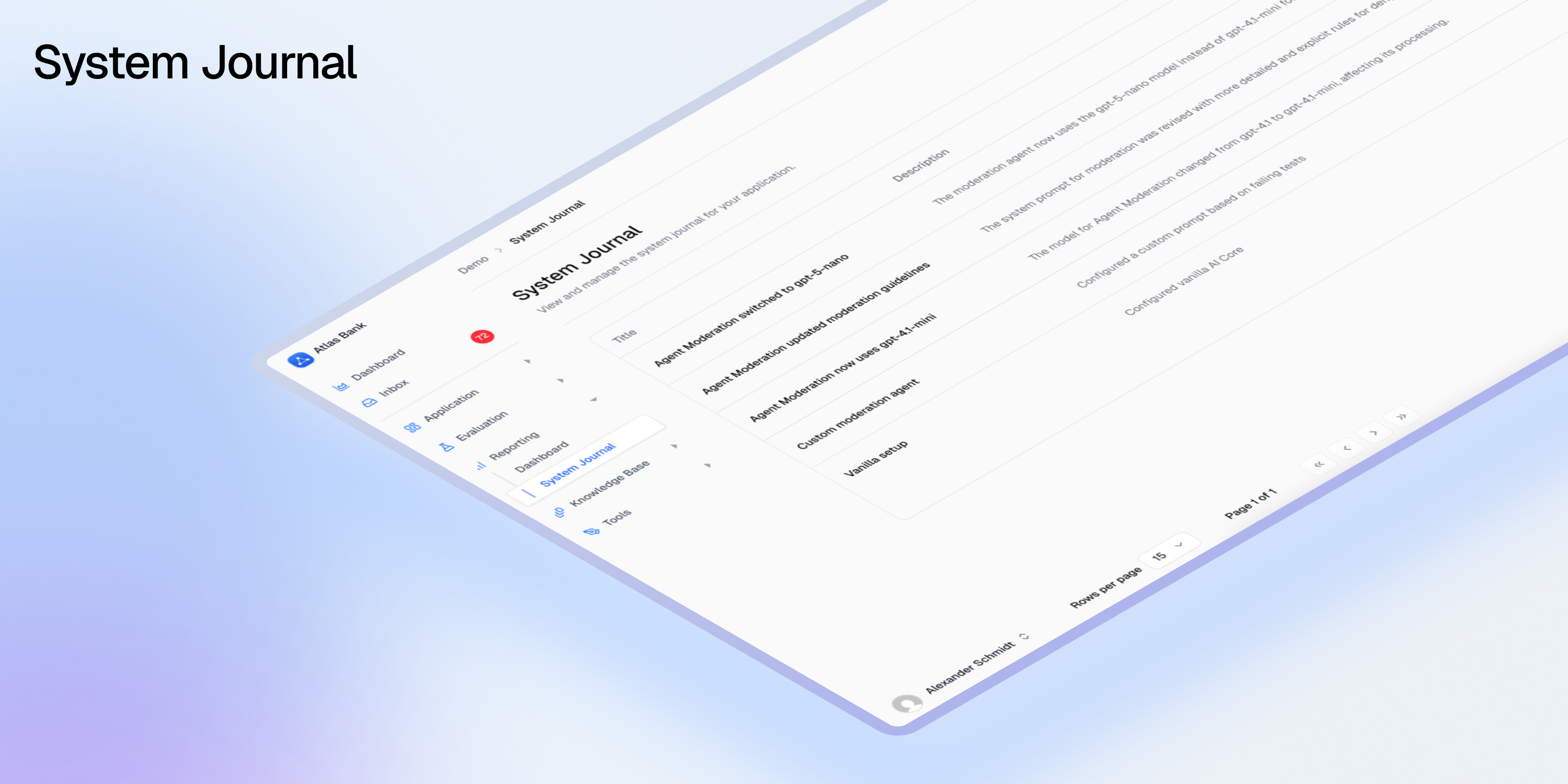
## What is the System Journal?
The System Journal is an intelligent monitoring system that automatically tracks and documents all significant changes in your AI model deployments. It serves as your automated compliance officer and operational guardian, creating a comprehensive audit trail of configuration changes, parameter modifications, and data anomalies across all your AI traces.
Think of it as a "black box recorder" for your AI systems—capturing every meaningful change that could impact model behavior, compliance, or evaluation accuracy.
### Key Capabilities
* **Automatic Change Detection**: Identifies when model parameters (temperature, max tokens, top-k, etc.) change between deployments
* **Missing Parameter Alerts**: Flags when critical parameters required for evaluation or compliance are absent
* **Intelligent Journal Entries**: Generates human-readable descriptions of what changed, when, and by how much
* **Complete Audit Trail**: Maintains a tamper-proof history of all configuration changes for regulatory compliance
* **Zero Manual Overhead**: Operates completely automatically in the background
## Why Use the System Journal?
### For Engineering Teams
**Prevent Configuration Drift**
You'll immediately know when model parameters change unexpectedly. No more debugging mysterious behavior changes or performance degradations caused by unnoticed configuration updates.
**Accelerate Incident Response**
When something goes wrong, the System Journal provides instant visibility into what changed and when. Instead of digging through logs, you can see at a glance: "LLM Temperature Changed: 0.4 → 0.9" with timestamps and context.
**Maintain Evaluation Integrity**
Missing parameters can invalidate your evaluation results. The System Journal ensures you catch these gaps before they impact your metrics or decision-making.
### For Compliance Teams
**Regulatory Readiness**
Financial institutions face strict requirements for AI transparency and explainability. The System Journal automatically maintains the comprehensive audit trails regulators expect, reducing preparation time from weeks to minutes.
**Risk Management**
Track when risk-relevant parameters change (like content filtering thresholds or decision boundaries) and ensure they stay within approved ranges.
**Evidence Collection**
Every journal entry includes timestamps, before/after values, and trace context—everything needed for compliance reporting or incident investigation.
### Real-World Impact
Consider this scenario: A wealth management firm's AI-powered client communication system suddenly starts generating longer, more creative responses. Without the System Journal, this could go unnoticed for weeks. With it, compliance immediately sees: "LLM Temperature Changed: 0.2 → 0.8" and "Max Tokens Changed: 150 → 500"—catching a potentially risky configuration change before it impacts clients.
## How to Use the System Journal
### Accessing the System Journal
1. Navigate to the **System Journal** section in your Avido dashboard
2. You'll see a chronological list of all journal entries across your AI systems
### Understanding Journal Entries
Each System Journal entry includes:
* **Type Indicator**: Visual icon showing the category (change, missing parameter, error)
* **Clear Description**: Plain-language explanation like "Model version changed from gpt-4-turbo to gpt-4o"
* **Timestamp**: Exact time the change was detected
* **Trace Link**: Direct connection to the affected trace for deeper investigation
* **Change Details**: Before and after values for parameter changes
### Viewing Journal Entries in Context
#### On the Dashboard
System Journal entries appear as reference lines on your metric graphs, showing exactly when changes occurred relative to performance shifts.
#### In Trace Details
When viewing individual traces, associated journal entries are displayed inline, providing immediate context for that specific execution.
#### In the System Journal List
The dedicated System Journal page provides:
* Filtering by entry type, date range, or affected system
* Sorting by relevance, time, or severity
* Bulk actions for reviewing multiple entries
### Common Workflows
#### Investigating Performance Changes
1. Notice a metric shift on your dashboard
2. Check for System Journal markers at the same timestamp
3. Click through to see what parameters changed
4. Review the trace details to understand the impact
#### Compliance Review
1. Access the System Journal for your reporting period
2. Filter by the relevant AI system or model
3. Export the journal entries for your compliance report
4. Document any required explanations or approvals
#### Responding to Alerts
When the System Journal detects missing required parameters:
1. The entry clearly identifies what's missing (e.g., "Missing Parameter: topK")
2. Click through to the affected trace
3. Update your configuration to include the missing parameter
4. Verify the fix in subsequent traces
### Best Practices
**Regular Review Schedule**
Set up a weekly review of System Journal entries to catch trends before they become issues.
**Tag Critical Parameters**
Work with your compliance team to identify which parameters are critical for your use case, ensuring the System Journal prioritizes these in its monitoring.
**Integrate with Your Workflow**
* Set up alerts for critical changes
* Include System Journal reviews in your deployment checklist
* Reference journal entries in incident post-mortems
**Use Journal Entries for Documentation**
The System Journal creates a natural documentation trail. Use it to:
* Track experiment results
* Document approved configuration changes
* Build a knowledge base of parameter impacts
### Advanced Features
#### Entry Classification
Different System Journal entry types use distinct visual indicators:
* 🔄 **Configuration Changes**: Parameter modifications
* ⚠️ **Missing Data**: Required fields not present
* 🔍 **Anomalies**: Unusual patterns detected
* ✅ **Resolutions**: Issues that have been addressed
#### Intelligent Grouping
When multiple parameters change simultaneously, the System Journal groups related changes into a single entry for easier understanding.
#### Historical Analysis
Compare current configurations against any point in history to understand evolution and drift over time.
## Getting Started
1. **No Setup Required**: The System Journal begins working automatically as soon as you start sending traces to Avido
2. **First Journal Entries**: You'll see your first entries within minutes of trace ingestion
3. **Customization**: Contact your Avido representative to configure specific parameters to monitor or adjust sensitivity thresholds
The System Journal transforms AI observability from reactive firefighting to proactive governance, ensuring your AI deployments remain compliant, performant, and predictable.
# Tracing
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/traces
Capture every step of your LLM workflow and send it to Avido for replay, evaluation, and monitoring.
When your chatbot conversation or agent run is in flight, **every action becomes an *event***.\
Bundled together they form a **trace** – a structured replay of what happened, step‑by‑step.
| Event | When to use |
| ----------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| `trace` | The root container for a whole conversation / agent run. |
| `llm` | Start and end of every LLM call. |
| `tool` | Calls to a function / external tool invoked by the model. |
| `retriever` | RAG queries and the chunks they return. |
| `log` | Anything else worth seeing while debugging (system prompts, branches, errors…). |
The full schema lives in API ▸ Ingestion.
***
## Recommended workflow
1. **Collect events in memory** as they happen.
2. **Flush** once at the end (or on fatal error).
3. **Add a `log` event** describing the error if things blow up.
4. **Keep tracing async** – never block your user.
5. **Evaluation‑only mode?** Only ingest when the run came from an Avido test → check for `testId` from the [Webhook](/webhooks).
6. **LLM events** should contain the *raw* prompt & completion – strip provider JSON wrappers.
***
## Ingesting events
You can send events:
* **Directly via HTTP**
* **Via our SDKs** (`avido`)
When authenticating with an API key, include both the `x-api-key` and `x-application-id`
headers. The application ID should match the application that owns the key so the
request can be authorized.
```bash cURL (default) theme={null}
curl --request POST \
--url https://api.avidoai.com/v0/ingest \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--header 'x-application-id: ' \
--header 'x-api-key: ' \
--data '{
"events": [
{
"type": "trace",
"timestamp": "2025-05-15T12:34:56.123455Z",
"referenceId": "123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426614174000",
"metadata": {
"source": "chatbot"
}
},
{
"type": "llm",
"event": "start",
"traceId": "123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426614174000",
"timestamp": "2025-05-15T12:34:56.123456Z",
"modelId": "gpt-4o-2024-08-06",
"params": {
"temperature": 1.2
},
"input": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "Tell me a joke."
}
]
}
]
}'
```
```ts Node theme={null}
import Avido from 'avido';
const client = new Avido({
applicationId: 'My Application ID',
apiKey: process.env['AVIDO_API_KEY'], // optional – defaults to env
});
const ingest = await client.ingest.create({
events: [
{
timestamp: '2025-05-15T12:34:56.123456Z',
type: 'trace',
testId: 'INSERT UUID'
},
{
timestamp: '2025-05-15T12:34:56.123456Z',
type: 'tool',
toolInput: 'the input to a tool call',
toolOutput: 'the output from the tool call'
}
],
});
console.log(ingest.data);
```
```python Python theme={null}
import os
from avido import Avido
client = Avido(
application_id=os.environ.get("AVIDO_APPLICATION_ID"),
api_key=os.environ.get("AVIDO_API_KEY"), # optional – defaults to env
)
ingest = client.ingest.create(
events=[
{
"timestamp": "2025-05-15T12:34:56.123456Z",
"type": "trace",
},
{
"timestamp": "2025-05-15T12:34:56.123456Z",
"type": "trace",
},
],
)
print(ingest.data)
```
***
## Tip: map your IDs
If you already track a conversation / run in your own DB, pass that same ID as `referenceId`.\
It makes liftover between your system and Avido effortless.
***
## Next steps
* Inspect traces in **Traces** inside the dashboard.
Need more examples or have a tricky edge case? [Contact us](mailto:support@avidoai.com) and we’ll expand the docs! 🎯
# Webhooks
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/webhooks
Trigger automated Avido tests from outside your code and validate payloads securely.
## Why webhook‑triggered tests?
**Part of Avido's secret sauce is that you can kick off a test *without touching your code*.**\
Instead of waiting for CI or redeploys, Avido sends an HTTP `POST` to an endpoint that **you** control.
| Benefit | What it unlocks |
| ----------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------- |
| **Continuous coverage** | Run tests on prod/staging as often as you like and automated. |
| **SME‑friendly** | Non‑developers trigger & tweak tasks from the Avido UI. |
***
## How it works
1. **A test is triggered** in the dashboard or automatically.
2. **Avido POSTs** to your configured endpoint.
3. **Validate** the `signature` + `timestamp` with our API/SDK.
4. **Run your LLM flow** using `prompt` from the payload.
5. **Emit a trace** that includes `testId` to connect results in Avido.
6. **Return `200 OK`** – any other status tells Avido the test failed.
Validating a webhook with the API requires both `x-api-key` and `x-application-id`
headers. Use the application ID that issued the API key.
### Payload example
When Avido triggers your webhook endpoint, it sends:
```json Webhook payload theme={null}
{
"prompt": "Write a concise onboarding email for new users.",
"testId": "123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426614174000",
"metadata": {
"customerId": "1",
"priority": "high"
}
}
```
Headers:
| Header | Purpose |
| ------------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------- |
| `x-avido-signature` | HMAC signature of the payload |
| `x-avido-timestamp` | Unix ms timestamp (in milliseconds) the request was signed |
**Notes:**
* `testId` is optional and only included when running actual tests
* `metadata` is optional and only included when available from the originating task
***
## Verification flow
```mermaid theme={null}
sequenceDiagram
Avido->>Your Endpoint: POST payload + headers
Your Endpoint->>Avido API: /v0/validate-webhook
Avido API-->>Your Endpoint: { valid: true }
Your Endpoint->>LLM: run(prompt)
Your Endpoint->>Avido Traces API: POST /v0/traces (testId)
```
If validation fails, respond **401** (or other 4xx/5xx). Avido marks the test as **failed**.
***
## Code examples
```bash cURL (default) theme={null}
curl --request POST --url https://api.avidoai.com/v0/validate-webhook --header 'Content-Type: application/json' --header 'x-application-id: ' --header 'x-api-key: ' --data '{
"signature": "abc123signature",
"timestamp": 1687802842609,
"body": {
"prompt": "Write a concise onboarding email for new users.",
"testId": "123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426614174000",
"metadata": {
"customerId": "1",
"priority": "high"
}
}
}'
```
```ts Node theme={null}
import express from 'express';
import { Avido } from '@avidoai/sdk-node';
const app = express();
app.use(express.json());
const client = new Avido({
applicationId: process.env.AVIDO_APPLICATION_ID!,
apiKey: process.env.AVIDO_API_KEY!,
});
app.post('/avido/webhook', async (req, res) => {
const signature = req.get('x-avido-signature');
const timestamp = req.get('x-avido-timestamp');
const body = req.body;
try {
const { valid } = await client.validateWebhook({
signature,
timestamp,
body
});
if (!valid) return res.status(401).send('Invalid webhook');
const result = await runAgent(body.prompt); // 🤖 your LLM call
await client.traces.create({
testId: body.testId,
input: body.prompt,
output: result
});
return res.status(200).send('OK');
} catch (err) {
console.error(err);
return res.status(500).send('Internal error');
}
});
```
```python Python theme={null}
import os
from flask import Flask, request, jsonify
from avido import Avido
app = Flask(__name__)
client = Avido(
application_id=os.environ["AVIDO_APPLICATION_ID"],
api_key=os.environ["AVIDO_API_KEY"],
)
@app.route("/avido/webhook", methods=["POST"])
def handle_webhook():
body = request.get_json(force=True) or {}
signature = request.headers.get("x-avido-signature")
timestamp = request.headers.get("x-avido-timestamp")
if not signature or not timestamp:
return jsonify({"error": "Missing signature or timestamp"}), 400
try:
resp = client.validate_webhook.validate(
signature=signature,
timestamp=timestamp,
body=body
)
if not resp.valid:
return jsonify({"error": "Invalid webhook signature"}), 401
except Exception as e:
return jsonify({"error": str(e)}), 401
result = run_agent(body.get("prompt")) # your LLM pipeline
client.traces.create(
test_id=body.get("testId"),
input=body.get("prompt"),
output=result
)
return jsonify({"status": "ok"}), 200
```
***
## Next steps
* Send us [Trace events](/traces).
* Schedule or manually tasks from **Tasks** in the dashboard.
* Invite teammates so they can craft evals and eyeball results directly in Avido.
***
1. **Avido sends a webhook** – When a test is triggered, Avido sends a POST request to your endpoint with synthetic input and a testId.
2. **You validate the request** – Verify the webhook signature to ensure it's really from Avido.
3. **Run your AI workflow** – Process the synthetic input through your normal application flow.
4. **Log events along the way** – Capture LLM calls, tool usage, retrievals, and other key steps.
5. **Send the trace to Avido** – When your workflow completes, send the full event trace back to Avido.
6. **View evaluation results** – Avido runs your configured evaluations and displays results in the dashboard.
***
## Getting Started
1. **Install an SDK**
```bash theme={null}
npm i @avidoai/sdk-node # Node
pip install avido # Python
```
2. **Setup a webhook endpoint** in your application [Learn more](/webhooks)
3. **Start tracing events** in your application [Learn more](/traces)
4. **Create your knowledge base** with Documents [Learn more](/documents)
```ts theme={null}
client.ingest.create({ events })
```
5. **Upload existing data** to auto-generate test cases and evaluations [Learn more](/quickstart)
6. **Review your baseline performance** in the dashboard
> Prefer pure HTTP? All endpoints are [documented here](/api-reference).
***
## Core concepts
| Concept | TL;DR |
| ------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| **Tests** | Automated runs of your workflow using synthetic input without exposing customer data. |
| **Tasks** | Test cases that can be auto-generated from existing data or created manually. |
| **Webhooks** | Avido triggers tests via POST requests – automated or through the UI. |
| **Traces** | Ordered lists of events that reconstruct a conversation / agent run. |
| **Events** | Atomic pieces of work (`llm`, `tool`, `retriever`, `log`). |
| **Evaluations** | Built-in metrics + custom business logic tests created without code. |
| **Documents** | Version-controlled, RAG-ready content that powers your AI's knowledge base. |
| **Inbox** | Central hub where all issues are captured, summarized, and triaged automatically. |
| **System Journal** | Automatic log of configuration changes and their impact on performance. |
Dive deeper with the sidebar or jump straight to **[Traces](/traces)** to see how instrumentation works.
***
## Need help?
* **Email** – [support@avidoai.com](mailto:support@avidoai.com)
Happy building! ✨
# System Journal
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/system-journal
Automated monitoring and documentation of AI model changes for compliance and operational excellence

## What is the System Journal?
The System Journal is an intelligent monitoring system that automatically tracks and documents all significant changes in your AI model deployments. It serves as your automated compliance officer and operational guardian, creating a comprehensive audit trail of configuration changes, parameter modifications, and data anomalies across all your AI traces.
Think of it as a "black box recorder" for your AI systems—capturing every meaningful change that could impact model behavior, compliance, or evaluation accuracy.
### Key Capabilities
* **Automatic Change Detection**: Identifies when model parameters (temperature, max tokens, top-k, etc.) change between deployments
* **Missing Parameter Alerts**: Flags when critical parameters required for evaluation or compliance are absent
* **Intelligent Journal Entries**: Generates human-readable descriptions of what changed, when, and by how much
* **Complete Audit Trail**: Maintains a tamper-proof history of all configuration changes for regulatory compliance
* **Zero Manual Overhead**: Operates completely automatically in the background
## Why Use the System Journal?
### For Engineering Teams
**Prevent Configuration Drift**
You'll immediately know when model parameters change unexpectedly. No more debugging mysterious behavior changes or performance degradations caused by unnoticed configuration updates.
**Accelerate Incident Response**
When something goes wrong, the System Journal provides instant visibility into what changed and when. Instead of digging through logs, you can see at a glance: "LLM Temperature Changed: 0.4 → 0.9" with timestamps and context.
**Maintain Evaluation Integrity**
Missing parameters can invalidate your evaluation results. The System Journal ensures you catch these gaps before they impact your metrics or decision-making.
### For Compliance Teams
**Regulatory Readiness**
Financial institutions face strict requirements for AI transparency and explainability. The System Journal automatically maintains the comprehensive audit trails regulators expect, reducing preparation time from weeks to minutes.
**Risk Management**
Track when risk-relevant parameters change (like content filtering thresholds or decision boundaries) and ensure they stay within approved ranges.
**Evidence Collection**
Every journal entry includes timestamps, before/after values, and trace context—everything needed for compliance reporting or incident investigation.
### Real-World Impact
Consider this scenario: A wealth management firm's AI-powered client communication system suddenly starts generating longer, more creative responses. Without the System Journal, this could go unnoticed for weeks. With it, compliance immediately sees: "LLM Temperature Changed: 0.2 → 0.8" and "Max Tokens Changed: 150 → 500"—catching a potentially risky configuration change before it impacts clients.
## How to Use the System Journal
### Accessing the System Journal
1. Navigate to the **System Journal** section in your Avido dashboard
2. You'll see a chronological list of all journal entries across your AI systems
### Understanding Journal Entries
Each System Journal entry includes:
* **Type Indicator**: Visual icon showing the category (change, missing parameter, error)
* **Clear Description**: Plain-language explanation like "Model version changed from gpt-4-turbo to gpt-4o"
* **Timestamp**: Exact time the change was detected
* **Trace Link**: Direct connection to the affected trace for deeper investigation
* **Change Details**: Before and after values for parameter changes
### Viewing Journal Entries in Context
#### On the Dashboard
System Journal entries appear as reference lines on your metric graphs, showing exactly when changes occurred relative to performance shifts.
#### In Trace Details
When viewing individual traces, associated journal entries are displayed inline, providing immediate context for that specific execution.
#### In the System Journal List
The dedicated System Journal page provides:
* Filtering by entry type, date range, or affected system
* Sorting by relevance, time, or severity
* Bulk actions for reviewing multiple entries
### Common Workflows
#### Investigating Performance Changes
1. Notice a metric shift on your dashboard
2. Check for System Journal markers at the same timestamp
3. Click through to see what parameters changed
4. Review the trace details to understand the impact
#### Compliance Review
1. Access the System Journal for your reporting period
2. Filter by the relevant AI system or model
3. Export the journal entries for your compliance report
4. Document any required explanations or approvals
#### Responding to Alerts
When the System Journal detects missing required parameters:
1. The entry clearly identifies what's missing (e.g., "Missing Parameter: topK")
2. Click through to the affected trace
3. Update your configuration to include the missing parameter
4. Verify the fix in subsequent traces
### Best Practices
**Regular Review Schedule**
Set up a weekly review of System Journal entries to catch trends before they become issues.
**Tag Critical Parameters**
Work with your compliance team to identify which parameters are critical for your use case, ensuring the System Journal prioritizes these in its monitoring.
**Integrate with Your Workflow**
* Set up alerts for critical changes
* Include System Journal reviews in your deployment checklist
* Reference journal entries in incident post-mortems
**Use Journal Entries for Documentation**
The System Journal creates a natural documentation trail. Use it to:
* Track experiment results
* Document approved configuration changes
* Build a knowledge base of parameter impacts
### Advanced Features
#### Entry Classification
Different System Journal entry types use distinct visual indicators:
* 🔄 **Configuration Changes**: Parameter modifications
* ⚠️ **Missing Data**: Required fields not present
* 🔍 **Anomalies**: Unusual patterns detected
* ✅ **Resolutions**: Issues that have been addressed
#### Intelligent Grouping
When multiple parameters change simultaneously, the System Journal groups related changes into a single entry for easier understanding.
#### Historical Analysis
Compare current configurations against any point in history to understand evolution and drift over time.
## Getting Started
1. **No Setup Required**: The System Journal begins working automatically as soon as you start sending traces to Avido
2. **First Journal Entries**: You'll see your first entries within minutes of trace ingestion
3. **Customization**: Contact your Avido representative to configure specific parameters to monitor or adjust sensitivity thresholds
The System Journal transforms AI observability from reactive firefighting to proactive governance, ensuring your AI deployments remain compliant, performant, and predictable.
# Tracing
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/traces
Capture every step of your LLM workflow and send it to Avido for replay, evaluation, and monitoring.
When your chatbot conversation or agent run is in flight, **every action becomes an *event***.\
Bundled together they form a **trace** – a structured replay of what happened, step‑by‑step.
| Event | When to use |
| ----------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| `trace` | The root container for a whole conversation / agent run. |
| `llm` | Start and end of every LLM call. |
| `tool` | Calls to a function / external tool invoked by the model. |
| `retriever` | RAG queries and the chunks they return. |
| `log` | Anything else worth seeing while debugging (system prompts, branches, errors…). |
The full schema lives in API ▸ Ingestion.
***
## Recommended workflow
1. **Collect events in memory** as they happen.
2. **Flush** once at the end (or on fatal error).
3. **Add a `log` event** describing the error if things blow up.
4. **Keep tracing async** – never block your user.
5. **Evaluation‑only mode?** Only ingest when the run came from an Avido test → check for `testId` from the [Webhook](/webhooks).
6. **LLM events** should contain the *raw* prompt & completion – strip provider JSON wrappers.
***
## Ingesting events
You can send events:
* **Directly via HTTP**
* **Via our SDKs** (`avido`)
When authenticating with an API key, include both the `x-api-key` and `x-application-id`
headers. The application ID should match the application that owns the key so the
request can be authorized.
```bash cURL (default) theme={null}
curl --request POST \
--url https://api.avidoai.com/v0/ingest \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--header 'x-application-id: ' \
--header 'x-api-key: ' \
--data '{
"events": [
{
"type": "trace",
"timestamp": "2025-05-15T12:34:56.123455Z",
"referenceId": "123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426614174000",
"metadata": {
"source": "chatbot"
}
},
{
"type": "llm",
"event": "start",
"traceId": "123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426614174000",
"timestamp": "2025-05-15T12:34:56.123456Z",
"modelId": "gpt-4o-2024-08-06",
"params": {
"temperature": 1.2
},
"input": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "Tell me a joke."
}
]
}
]
}'
```
```ts Node theme={null}
import Avido from 'avido';
const client = new Avido({
applicationId: 'My Application ID',
apiKey: process.env['AVIDO_API_KEY'], // optional – defaults to env
});
const ingest = await client.ingest.create({
events: [
{
timestamp: '2025-05-15T12:34:56.123456Z',
type: 'trace',
testId: 'INSERT UUID'
},
{
timestamp: '2025-05-15T12:34:56.123456Z',
type: 'tool',
toolInput: 'the input to a tool call',
toolOutput: 'the output from the tool call'
}
],
});
console.log(ingest.data);
```
```python Python theme={null}
import os
from avido import Avido
client = Avido(
application_id=os.environ.get("AVIDO_APPLICATION_ID"),
api_key=os.environ.get("AVIDO_API_KEY"), # optional – defaults to env
)
ingest = client.ingest.create(
events=[
{
"timestamp": "2025-05-15T12:34:56.123456Z",
"type": "trace",
},
{
"timestamp": "2025-05-15T12:34:56.123456Z",
"type": "trace",
},
],
)
print(ingest.data)
```
***
## Tip: map your IDs
If you already track a conversation / run in your own DB, pass that same ID as `referenceId`.\
It makes liftover between your system and Avido effortless.
***
## Next steps
* Inspect traces in **Traces** inside the dashboard.
Need more examples or have a tricky edge case? [Contact us](mailto:support@avidoai.com) and we’ll expand the docs! 🎯
# Webhooks
Source: https://docs.avidoai.com/webhooks
Trigger automated Avido tests from outside your code and validate payloads securely.
## Why webhook‑triggered tests?
**Part of Avido's secret sauce is that you can kick off a test *without touching your code*.**\
Instead of waiting for CI or redeploys, Avido sends an HTTP `POST` to an endpoint that **you** control.
| Benefit | What it unlocks |
| ----------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------- |
| **Continuous coverage** | Run tests on prod/staging as often as you like and automated. |
| **SME‑friendly** | Non‑developers trigger & tweak tasks from the Avido UI. |
***
## How it works
1. **A test is triggered** in the dashboard or automatically.
2. **Avido POSTs** to your configured endpoint.
3. **Validate** the `signature` + `timestamp` with our API/SDK.
4. **Run your LLM flow** using `prompt` from the payload.
5. **Emit a trace** that includes `testId` to connect results in Avido.
6. **Return `200 OK`** – any other status tells Avido the test failed.
Validating a webhook with the API requires both `x-api-key` and `x-application-id`
headers. Use the application ID that issued the API key.
### Payload example
When Avido triggers your webhook endpoint, it sends:
```json Webhook payload theme={null}
{
"prompt": "Write a concise onboarding email for new users.",
"testId": "123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426614174000",
"metadata": {
"customerId": "1",
"priority": "high"
}
}
```
Headers:
| Header | Purpose |
| ------------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------- |
| `x-avido-signature` | HMAC signature of the payload |
| `x-avido-timestamp` | Unix ms timestamp (in milliseconds) the request was signed |
**Notes:**
* `testId` is optional and only included when running actual tests
* `metadata` is optional and only included when available from the originating task
***
## Verification flow
```mermaid theme={null}
sequenceDiagram
Avido->>Your Endpoint: POST payload + headers
Your Endpoint->>Avido API: /v0/validate-webhook
Avido API-->>Your Endpoint: { valid: true }
Your Endpoint->>LLM: run(prompt)
Your Endpoint->>Avido Traces API: POST /v0/traces (testId)
```
If validation fails, respond **401** (or other 4xx/5xx). Avido marks the test as **failed**.
***
## Code examples
```bash cURL (default) theme={null}
curl --request POST --url https://api.avidoai.com/v0/validate-webhook --header 'Content-Type: application/json' --header 'x-application-id: ' --header 'x-api-key: ' --data '{
"signature": "abc123signature",
"timestamp": 1687802842609,
"body": {
"prompt": "Write a concise onboarding email for new users.",
"testId": "123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426614174000",
"metadata": {
"customerId": "1",
"priority": "high"
}
}
}'
```
```ts Node theme={null}
import express from 'express';
import { Avido } from '@avidoai/sdk-node';
const app = express();
app.use(express.json());
const client = new Avido({
applicationId: process.env.AVIDO_APPLICATION_ID!,
apiKey: process.env.AVIDO_API_KEY!,
});
app.post('/avido/webhook', async (req, res) => {
const signature = req.get('x-avido-signature');
const timestamp = req.get('x-avido-timestamp');
const body = req.body;
try {
const { valid } = await client.validateWebhook({
signature,
timestamp,
body
});
if (!valid) return res.status(401).send('Invalid webhook');
const result = await runAgent(body.prompt); // 🤖 your LLM call
await client.traces.create({
testId: body.testId,
input: body.prompt,
output: result
});
return res.status(200).send('OK');
} catch (err) {
console.error(err);
return res.status(500).send('Internal error');
}
});
```
```python Python theme={null}
import os
from flask import Flask, request, jsonify
from avido import Avido
app = Flask(__name__)
client = Avido(
application_id=os.environ["AVIDO_APPLICATION_ID"],
api_key=os.environ["AVIDO_API_KEY"],
)
@app.route("/avido/webhook", methods=["POST"])
def handle_webhook():
body = request.get_json(force=True) or {}
signature = request.headers.get("x-avido-signature")
timestamp = request.headers.get("x-avido-timestamp")
if not signature or not timestamp:
return jsonify({"error": "Missing signature or timestamp"}), 400
try:
resp = client.validate_webhook.validate(
signature=signature,
timestamp=timestamp,
body=body
)
if not resp.valid:
return jsonify({"error": "Invalid webhook signature"}), 401
except Exception as e:
return jsonify({"error": str(e)}), 401
result = run_agent(body.get("prompt")) # your LLM pipeline
client.traces.create(
test_id=body.get("testId"),
input=body.get("prompt"),
output=result
)
return jsonify({"status": "ok"}), 200
```
***
## Next steps
* Send us [Trace events](/traces).
* Schedule or manually tasks from **Tasks** in the dashboard.
* Invite teammates so they can craft evals and eyeball results directly in Avido.
***